Archive
SQL DBA – Moved MASTER database by ALTER DATABASE statement? here’s the solution
Have you also moved your MASTER DATABASE by using “ALTER DATABASE” statement just like you did for other system databases like MSDB, MODEL, TEMPDB & other databases?
If YES, then you are same nerdy DBA like me.
For quite some time I was observing very bad performance in one of our DEV servers. So today I thought to check it, I found that the C: Drive is almost full. Don’t know why do the DBA guys installed SQL Server on C: drive and put all system databases here to make it even worse. To get some room on C: drive I thought to move all four system databases (i.e. MASTER, MODEL, MSDB & TEMPDB) to another drive.
So, I created normal “ALTER DATABASE” scripts for all the 4 databases and executed them, as follows:
ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'tempdev' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\tempdb.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'templog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\templog.ldf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'modeldev' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\modeldev.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'modellog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\modellog.ldf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'MSDBData' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\MSDBData.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'MSDBLog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\MSDBLog.ldf' ) -- !!!! BEWARE DON'T RUN THIS !!!! ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'master' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\master.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'mastlog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\mastlog.ldf' ) -- !!!! BEWARE DON'T RUN THIS !!!!
-> Happily I Stopped the SQL Server service.
-> Now, to move the databases physically I moved the MDF & LDF files to the new location I used in “ALTER DATABASE” statements above.
-> After moving DB files I tried to Start the “SQL Server” service, but the service didn’t start and I was getting following error:
“The SQL Server service on [SERVER_NAME] started and then stopped. blah blah blah…”
I immediately thought that I’ve done something wrong, checked MS BOL, and found that I should not have moved the MASTER database by using “ALTER DATABASE” statement.
–> WORKAROUND:
Now when the wrong scripts are executed and there is no way to undo it, there should be some way to fix it.
SQL Server comes with a tool i.e. “SQL Server Configuration Manager” to manage the services associated with SQL Server. Like, for this case to configure startup options that will be used every time the Database Engine starts in SQL Server.
Open this tool from “Program Files -> SQL Server -> Configuration Tools”:
-> Select “SQL Server Services” on the left side navigation bar.
-> On the right side Right Click on SQL Server instance and select Properties.
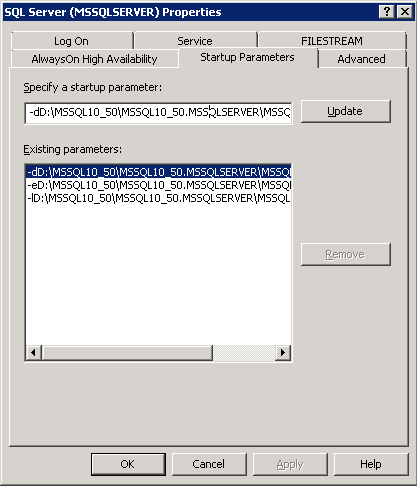
-> On the Pop-Up select the “Startup Paramaters” tab. Here you can change the MASTER database’s MDF & LDF file’s location:
—> Parameter starting with “-dD” is for DATA file (MDF).
—> AND parameter starting with “-lD” is for LOG file (LDF).
-> Select both properties one by one and change the file location at the “Existing Parameters:” text box and click Update for both the files.
-> Now, Start the Services and yes it started without any issue.
-> Check the new location by issuing either of following 2 SQL queries:
select * from sys.sysdatabases -- OR -- select * from sys.master_files
Not only this is a workaround to fix this issue, but you can also use this tool to move your MASTER database to a different Drive.
SQL Tips – Different ways to get SQL Server Version
Today I got an email form a newbee regarding some help in SQL Server.
His question was a typical “SQL Server Interview Question”: What are the various ways to get SQL Server version number?
So I researched a bit and come up with following different methods for the same, as follows:
–> Method #1:
select @@version
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (SP2) - 10.50.4000.0 (X64) Jun 28 2012 08:36:30 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation Data Center Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1) (Hypervisor)
–> Method #2:
SELECT
SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion') as ProductVersion,
SERVERPROPERTY ('productlevel') as ProductLevel,
SERVERPROPERTY ('edition') as Edition
ProductVersion ProductLevel Edition 10.50.4000.0 SP2 Data Center Edition (64-bit)
–> Method #3:
select CAST(@@microsoftversion as binary(10)) as VerBinary, @@microsoftversion / 0x01000000 as VersionNumber1, @@microsoftversion / power(2, 24) as VersionNumber2, @@microsoftversion & 0xFFFF as ReleaseNumber
VerBinary VersionNumber1 VersionNumber2 ReleaseNumber 0x0000000000000A320FA0 10 10 4000
–> Method #4:
EXEC xp_msver 'ProductVersion'
Index Name Internal_Value Character_Value 2 ProductVersion 655410 10.50.4000.0
–> Method #5:
EXEC sp_server_info
attribute_id attribute_name attribute_value 1 DBMS_NAME Microsoft SQL Server 2 DBMS_VER Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 - 10.50.4000.0 500 SYS_SPROC_VERSION 10.50.4000
–> Method #6:
Check the INSTANCE name in SSMS Object explorer. It shown SQL Server Version Number in brackets, like: (SQL Server 10.50.4000 – DOMAIN\user).
–> Method #7:
Check by “SQL Server Features Discovery report”.
Go to Start Menu -> Pragram Files -> Microsoft SQL Server -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Installation Center (64-bit)
A window will open, click on Toolsat the left navigation bar, then click on “Installed SQL Server Features Discovery report” link.
This will open up a HTML page in web-browser, which looks like in the image below:

–> Method #8:
Simply, in SSMS go to menu, Help -> About.
You will get a pop-up window which shows version number of difefrent Components installed as a part of SQL Server installation.
SQL DBA – Upgrade to SQL Server 2012 – Use Upgrade Advisor
Are you planning to upgrade your SQL Servers to 2012? YES!
How will you make sure that you are ready for Upgrade? ???
How will you make sure that the Upgrade will be seamless? 😦
SQL Server 2012 “Upgrade Advisor” is for you to check and analyze instances of all previous SQL Server versions i.e. 2008 R2, 2008, 2005 and even 2000 in preparation for upgrading to SQL Server 2012.
“Upgrade Advisor” identifies all features and configuration changes that might affect your upgrade. It provides links to documentation that describes each identified issue and how to resolve it and also generates a report that captures identified issues to fix either before or after you upgrade.
This tool has some prerequisites to install, and if you don’t install them you might see following error while installation:
Setup is missing prerequisites: -Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Transact-SQL Script DOM, which is not installed by Upgrade Advisor Setup. To continue, install SQL Server 2012 Transact-SQL Script DOM from below hyperlink and then run the Upgrade Advisor Setup operation again : Go to http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=216742
The above error mentions to install “MS SQL Server 2012 Transact-SQL ScriptDom” component. Install it from here: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=29065&ocid=aff-n-we-loc–ITPRO40886&WT.mc_id=aff-n-we-loc–ITPRO40886
But for this also “MS DOT NET 4.0” is required on your system. To Install it check this link: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=17851
After installing Upgrade Advisor, launch the tool, it gives you 2 options:
1. Launch Upgrade Advisor Analysis Wizard
2. Report Upgrade Advisor Viewer
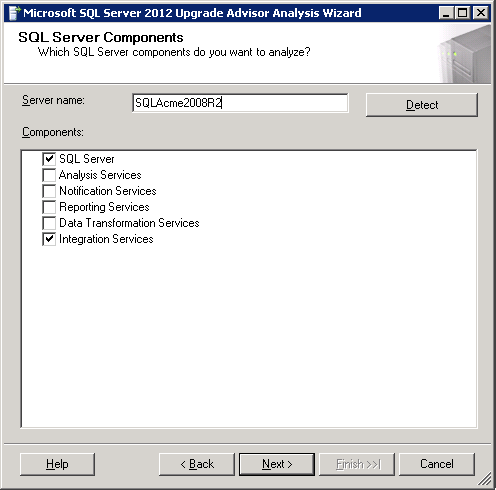
–> Analysis Wizard lets you run alanysis on following SQL components shown in image below:
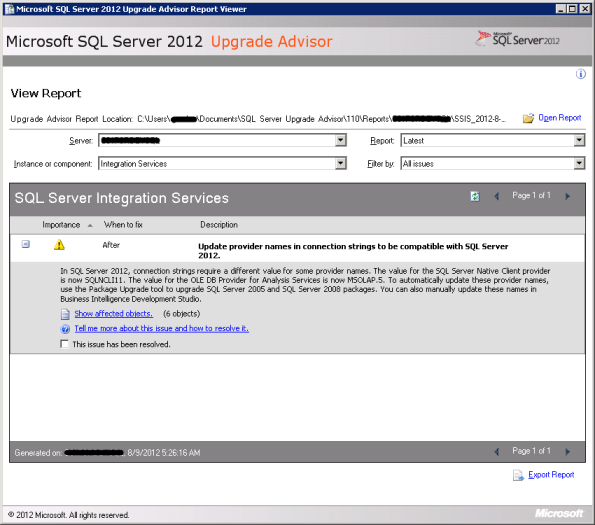
–> Report Viewer tell you about the changes that needs attention or needs change/fix before or after upgrading to 2012. After Analysis Wizard finishes it creates repots which is in the form of an XML file.
The Report Viewer tool uses this XML file generated and give you details of components that may be affected. The report provides Importance, When to fix (Before/After), Description and links to information that will help you fix or reduce the effect of the known issues, image below:
After you are done with this Analysis and checking Reports, now the time is to work and fix on issues listed in the Reports.
Other than this you also need to check Microsoft BOL and/or MSDN articles to check for Discontinued and Deprecated features, Breaking and Behavior Changes.
Check following important links:
1. SQL Server Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc707787
2. Database Engine Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143532
3. Analysis Services Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143479
4. Integration Services Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143706
5. Reporting Services Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143251
6. Other Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280407
SQL DBA – Check Isolation Level of a Database | DBCC USEROPTIONS
While testing a functionality we had to run some Stored Procedures in parallel. So we executed all 4 SPs in different Sessions (separate windows). All SPs got executed successfully except one, this one ended up in a Deadlock.
I thought to check the Isolation level of database but my mind didn’t clicked instantly.
So I checked MS BOL about this and find the DBCC management command to find it, which is DBCC USEROPTIONS & as follows:
USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO DBCC USEROPTIONS GO
Output:- Set Option Value textsize 2147483647 language us_english dateformat mdy datefirst 7 lock_timeout -1 quoted_identifier SET arithabort SET ansi_null_dflt_on SET ansi_warnings SET ansi_padding SET ansi_nulls SET concat_null_yields_null SET isolation level read committed
Other Isolation level values it returns are:-
- read uncommitted
- read committed
- repeatable read
- serializable
- read committed snapshot
- snapshot
The sys.databases metadata View also contains a column i.e. is_read_committed_snapshot_on, which tells if READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT Isolation level in ON or OFF.
Check this:
select is_read_committed_snapshot_on, * from sys.databases
SQL DBA – SHRINK DATABASE & SHRINK FILE – SQL Server
While working with huge databases with large tables there are times when you get your database and log files expand ridiculously and eating up the entire disks.
This happens when you are either on an:
– OLTP environment and doing lots of DMLs (INSERTS, UPDATES or DELETES) or
– OLAP environment when you are running huge SQL queries that goes on expanding your tempdb and finally eats up your entire drive space.
There are lot of ways to better configure your disks and databases there to avoid such situations. But these kind of situations come and you have to approach the DBA or become a DBA yourself.
Check the LOG Size and Space used, here:
DBCC SQLPERF (LOGSPACE)
Check if your database has adequate space available to free up:
SELECT name, size/128.0 - CAST(FILEPROPERTY(name, 'SpaceUsed') AS int)/128.0 AS AvailableSpaceInMB FROM sys.database_files;
Before shrinking the log file, it better to backup your transaction logs, as shown below:
BACKUP LOG <database_name> WITH TRUNCATE_ONLY DBCC SHRINKFILE(database_name_log, 2)
OR, you can simply change the Database recovery mode to Simple, and run the above mentioned DBCC statement.
tempdb can be freed up by simply restarting SQL Server. When SQL Server shuts down it deletes the tempdb and on restart it automatically creates tempdb database. Thus you get fresh tempdb with minimal space. This is not advisable on production servers and should be handled by experts.