Archive
Get Row Count of Insert/Update/Delete records in MERGE Statement – MSDN TSQL forum
–> Question:
How can I get the numbers of records affected in the Merge statement, INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE separately and store it in a variable so I can get it in the application side?
Thanks !
–> My Answer:
You need to use OUTPUT clause with MERGE statement, try this:
DECLARE @SummaryOfChanges TABLE(Change VARCHAR(20)); MERGE tblTarget AS Target USING (SELECT Col1,Col2 FROM tblSource) AS Source ON (Target.Col1 = Source.Col1) WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET target.Col2 = source.Col2 -- Need to get affected rows here WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET THEN INSERT (Col1,Col2) VALUES (Col1,Col2); -- Need to get affected rows here OUTPUT $action INTO @SummaryOfChanges; --< check here -- Get the count of Insert/Update/Delete'd records from the below table variable SELECT Change, COUNT(*) AS CountPerChange FROM @SummaryOfChanges GROUP BY Change;
For more info on MERGE and OUTPUT clause statement check this link: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb510625.aspx
SQL Server 2016 Install Error – Rule “Oracle JRE 7 Update 51 (64-bit) or higher is required for Polybase” failed
While installing SQL Server 2016/2017 with Polybase feature, you might have noticed this issue, and some of you would have no idea what to do next.
—————————
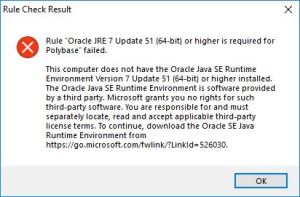
Rule Check Result
—————————
Rule “Oracle JRE 7 Update 51 (64-bit) or higher is required for Polybase” failed.This computer does not have the Oracle Java SE Runtime Environment Version 7 Update 51 (64-bit) or higher installed. The Oracle Java SE Runtime Environment is software provided by a third party. Microsoft grants you no rights for such third-party software. You are responsible for and must separately locate, read and accept applicable third-party license terms. To continue, download the Oracle SE Java Runtime Environment from https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=526030.
—————————
OK
—————————
–> This is because the new Polybase feature in SQL Server requires Java Runtimes or JRE.
1. You are installing SQL Server and you chose Polybase feature.
2. On the next Feature Rule page you get stuck with following error: Oracle JRE 7 Update 51 or higher is required, Failed.
3. You click on the Failed link it popped up an error box giving you more error details shown below:
- Error popup, Click to expand
.
4. You just need to click on the URL provided in the error popup box, or you can directly download it from [here].
5. You will be redirected to the Oracle JRE download page.
– Here you first need to Register/Login
– Accept the License Agreement
– Finally download the JRE EXE file.
6. After JRE installation is completed, just Re-run the Rules and it will be Passed this time, click Next.
–> You can also check this in video here:
New built-in function CONCAT_WS() in SQL Server 2017
In my previous posts I discussed new Functions introduced in SQL Server vNext (or 2018), like STRING_AGG(), TRIM(), TRANSLATE().
Here in this post I’ll discuss about one more new function i.e. CONCAT_WS(), here “_WS” means “With Separator”.
This is very similar to the existing CONCAT() function introduced back in SQL Server 2012, which concatenates a variable number of arguments or string values.
The difference is the new function CONCAT_WS() accepts a delimiter specified as the 1st argument, and thus there is no need to repeat the delimiter after very String value like in CONCAT() function.
Also the new CONCAT_WS() function takes care of NULL values and do not repeat the delimiter, which you can see in 2nd example below.
Syntax:
CONCAT_WS ( separator, argument1, argument1 [, argumentN]… )
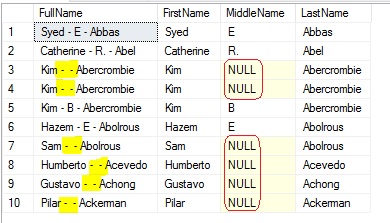
–> Example #1:
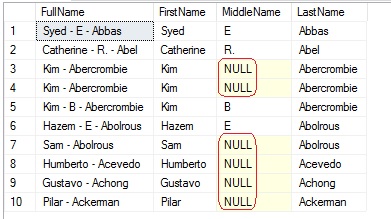
With CONCAT_WS() we will use the delimiter just once and it concatenates the names separated by ‘-‘, and do not repeat the hyphen where the middle name is NULL.
USE [AdventureWorks2014]
GO
SELECT TOP 10
CONCAT_WS(' - ', FirstName, MiddleName, LastName) as FullName,
FirstName, MiddleName, LastName
FROM [Person].[Person]
–> Example #2:
With CONCAT() the delimiter needs to be used after every argument, it concatenates the names separated by ‘-‘, do repeats the hyphen where the middle name is NULL.
SELECT TOP 10 CONCAT(FirstName, ' - ', MiddleName, ' - ', LastName) as FullName, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName FROM [Person].[Person]
New built-in function TRANSLATE() in SQL Server 2017
Microsoft looks very serious this time to move people from other databases to SQL Server. As with SQL Server 2016 & 2017 you can see lot of Built-in function added, which were present in other databases from long back, will ease database development in SQL Server.
One of this function is TRANSLATE() function, which can be used like a REPLACE() function, and would avoid using REPLACE() function multiple times in a query.
Syntax:
TRANSLATE ( inputString, characters, translations)
Note: characters and translations params should have same length.
–> Consider this example I’ve taken from MSDN:
SELECT TRANSLATE('2*[3+4]/{7-2}', '[]{}', '()()');
GO
Output:
| Input | Output |
| 2*[3+4]/{7-2} | 2*(3+4)/(7-2) |
–> If you had to do same with REPLACE() function then you would end up writing multiple & nested REPLACE() function, like:
SELECT
REPLACE(
REPLACE(
REPLACE(
REPLACE('2*[3+4]/{7-2}', '[', '('),
']', ')'),
'{', '('),
'}', ')');
GO
After working with this new feature it reminds me of IIF vs CASE statement. The IIF() function also works as a shortcut of CASE statement and cuts lot of clutter and gives you clean code.
Hope you find this small utility very handy while developing complex queries, will post more scenarios if I came across going forward, thanks !!!
New built-in function TRIM() in SQL Server 2017
If you are thinking the new TRIM() function in SQL Server 2017 is just a combination of LTRIM() & RTRIM() functions, then you are wrong :). It’s more than that and we will check it today !
– LTRIM() function is used to truncate all leading blanks, or white-spaces from the left side of the string.
– RTRIM() function is used to truncate all trailing blanks, or white-spaces from the right side of the string.
–> Now, with teh new TRIM() function you can do both, but more than that.
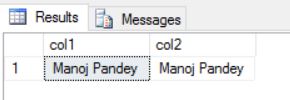
Usage #1: TRIM() function will truncate all leading & trailing blanks from a String:
SELECT
TRIM (' Manoj Pandey ') as col1,
LTRIM(RTRIM(' Manoj Pandey ')) as col2
Usage #2: Plus it can be used to remove specific characters from both sides of a String, like below:
SELECT TRIM ( 'm,y' FROM 'Manoj Pandey') as col1, TRIM ( 'ma,ey' FROM 'Manoj Pandey') as col2, TRIM ( 'm,a,e,y' FROM 'Manoj Pandey') as col3
Thus with the above query you can see that you can trim characters too, by providing leading & trailing characters, but should be in same sequence as your string is.
Also for Col2 & Col3 we have provided Trimming Characters in 2 different ways, but got the same output.
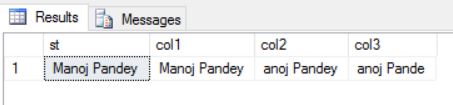
–> Note: I just mentioned above that the leading & trailing characters should be in same sequence. If you provide in different sequence like below you won’t get desired results.
SELECT 'Manoj Pandey' as st, TRIM ( 'a,n' FROM 'Manoj Pandey') as Col1, TRIM ( 'm,e' FROM 'Manoj Pandey') as Col2, TRIM ( 'm,o,y,e' FROM 'Manoj Pandey') as Col3
Like for Col3 you cannot get rid of middle characters (like ‘o’ and ‘n’) until and unless they become leading or trailing characters.