Archive
SQL Server 2012 (a.k.a Denali) – New feature | Enhanced OVER() Clause – Part1
OVER() clause in SQL Server was introduced in version 2005 and it was the same in 2008 and even 2008-R2.
Ranking functions like ROW_NUMBER(), RANK(), DENSE_RANK() & NTILE() can use the OVER() clause to Parition and Order a record-set before actually applying their logic. Thus a large record-set can be divided into several partitions and calculations can be applied to each set in a set-based approach rather than going with Loops or Cursors.
With the new version of SQL Server i.e. 2012 the OVER() clause has been extended completely to other aggregates, like SUM(), AVG(), etc. Prior to this the OVER() clause can be partially used for these Aggregate Functions.
Here we will see solving a classic problem of calculating Running Totals with this new feature.
I’ve already discussed about solving this problem with JOINS in version 2005,2008, 2008-R2 in my previous post at following [link].
Let’s see how can we use the SUM() Aggregate Function with OVER() clause to solve this:
USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO -- With 2012, calculating Running totals by using Aggregare function SUM() with extended Window Function OVER(): ;with RunTot as ( select row_number() over(order by s.OrderDate) as row, s.SalesPersonID, p.FirstName, p.LastName, s.TotalDue, s.OrderDate from Sales.SalesOrderHeader s join Person.Person p on s.SalesPersonID = p.BusinessEntityID ) SELECT SalesPersonID, FirstName, LastName, OrderDate, TotalDue, SUM(TotalDue) OVER(partition by SalesPersonID ORDER BY row) FROM RunTot order by SalesPersonID, row GO -- Prior to 2012 calculating Running totals by using SELF-JOIN: ;with RunTot as ( select row_number() over(partition by s.SalesPersonID order by s.OrderDate) as row, s.SalesPersonID, p.FirstName, p.LastName, s.TotalDue, s.OrderDate from Sales.SalesOrderHeader s join Person.Person p on s.SalesPersonID = p.BusinessEntityID) select a.row, a.SalesPersonID, a.FirstName, a.LastName, a.OrderDate, a.TotalDue, sum(b.TotalDue) as RunTotal from RunTot a join RunTot b on a.SalesPersonID = b.SalesPersonID and a.row >= b.row group by a.row, a.SalesPersonID, a.FirstName, a.LastName, a.TotalDue, a.OrderDate order by a.SalesPersonID, a.row
On comparing performance of both the queries within the batch:
– The first query with SUM() window function costs just 38%.
– While the second query without the SUM() window function by using JOINS costs 68%.
I still like to call SQL Server’s latest release by its code name “Denali”, not “SQL Server 2012”.
Stay tuned to other new features of Denali in my forthcomming posts.
For more information about the OVER() clause check MS BOL link here: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189461.aspx
SQL Server 2012 (a.k.a Denali) – New feature | WITH RESULT SETS
“WITH RESULT SETS”, a new feature added in SQL Server 2012 allows us to tweak the Column Names and their Datatypes returned by an SP upon executed as per our needs. In SQL Server 2012 while calling an SP you can add the “WITH RESULT SETS” option and can provide the new Column Names and/or with new Datatypes with the parenthesis as per your wish (shown below).
Prior to this if one has to do the same, he has to either:
– Edit the same SP with new column names, or
– Create a new duplicate SP with different column headers, or
– Push records to a temp table first then use the records set form that table (discussed in later part of this post).
Let’s check this new feature by a simple example here by using a Stored Procedure from [AdventureWorks2012] database for SQL Server 2012:
USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO -- Normal SP call without using "WITH RESULT SETS" option: EXEC [dbo].[uspGetEmployeeManagers] @BusinessEntityID = 100
Recordset with same headers as in SP: RecursionLevel BusinessEntityID FirstName LastName OrganizationNode ManagerFirstName ManagerLastName 0 100 Lolan Song /3/1/9/7/ Kok-Ho Loh 1 93 Kok-Ho Loh /3/1/9/ Peter Krebs 2 26 Peter Krebs /3/1/ James Hamilton 3 25 James Hamilton /3/ Ken Sánchez
-- This is how you can use the new option and get desired headers: EXEC [dbo].[uspGetEmployeeManagers] @BusinessEntityID = 100 WITH RESULT SETS ( ( Level INT, BusinessID INT, EmpFirstName VARCHAR(50), EmpLastName VARCHAR(50), OrgNode VARCHAR(20), ManagerFirstName VARCHAR(50), ManagerLastName VARCHAR(50) ) )
Recordset with new headers as in SP: Level BusinessID EmpFirstName EmpLastName OrgNode ManagerFirstName ManagerLastName 0 100 Lolan Song /3/1/9/7/ Kok-Ho Loh 1 93 Kok-Ho Loh /3/1/9/ Peter Krebs 2 26 Peter Krebs /3/1/ James Hamilton 3 25 James Hamilton /3/ Ken Sánchez
–> Traditonal appraoch prior to ver. 2012
-- Create a table with columns with required names: CREATE TABLE #tempData ( Level INT, BusinessID INT, EmployeeFirstName VARCHAR(50), EmployeeLastName VARCHAR(50), OrgNode VARCHAR(20), ManagerFirstName VARCHAR(50), ManagerLastName VARCHAR(50) ) -- Insert records from the SP to the table: INSERT INTO #tempData (Level, BusinessID, EmployeeFirstName, EmployeeLastName, OrgNode, ManagerFirstName, ManagerLastName) EXEC @return_value = [dbo].[uspGetEmployeeManagers] @BusinessEntityID = 100 -- Finaly select the table and use the records: SELECT * FROM #tempData -- Final Cleanup: DROP TABLE #tempData GO
Well this is OK, but not very exciting feature for me as a developer.
I was hoping this would allow me to add/remove the columns and/or Concatenate them, like FirstName & LastName to FullName, but No!!!
For more information you can check MS BOL, here: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188332(v=sql.110).aspx
SQL Server 2012 (a.k.a Denali) – New feature | FileTables
In my [previous posts] I discussed about new features of Denali, now SQL Server 2012.
Here, in this post I’ll talk about a new feature that I explored recently, when I was working with creating tables in SQL Server 2012. I observed a new item in object explorer that took my attention and created eagerness to explore it, and that new thing is FileTables.
As per MS BOL, The new FileTable feature brings support for the Windows file namespace and compatibility with Windows applications to the file data stored in SQL Server. FileTable lets an application integrate its storage and data management components, and provides integrated SQL Server services – including full-text search and semantic search – over unstructured data and metadata.
In other words, you can store files and documents in special tables in SQL Server called FileTables, but access them from Windows applications as if they were stored in the file system, without making any changes to your client applications. The FileTable feature builds on top of SQL Server FILESTREAM technology.
–> Let’s see how can we use this new feature by a simple example below:
USE [master] GO -- Create a new Database with Filestream enabled: CREATE DATABASE [newFileStreamDB] CONTAINMENT = NONE ON PRIMARY ( NAME = N'newFileStreamDB', FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.MSSQLSERVER12RC0\MSSQL\DATA\newFileStreamDB.mdf' , SIZE = 5120KB , MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED, FILEGROWTH = 1024KB ), FILEGROUP newFileStreamGroup CONTAINS FILESTREAM DEFAULT ( NAME = newFileStreamGroupFiles, FILENAME= 'D:\SQL_Server2012\FileTables\Files', MAXSIZE = UNLIMITED ) LOG ON ( NAME = N'newFileStreamDB_log', FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.MSSQLSERVER12RC0\MSSQL\DATA\newFileStreamDB_log.ldf' , SIZE = 1024KB , MAXSIZE = 2048GB , FILEGROWTH = 10% ) WITH FILESTREAM ( NON_TRANSACTED_ACCESS = FULL, DIRECTORY_NAME = N'FileTables' ) GO -- Use the new Database: USE [newFileStreamDB] GO -- Creating a new FileTable CREATE TABLE [dbo].[firstFileTable] AS FILETABLE ON [PRIMARY] FILESTREAM_ON [newFileStreamGroup] WITH ( FILETABLE_DIRECTORY = N'myfirstFileTable', FILETABLE_COLLATE_FILENAME = Latin1_General_CI_AI ) GO
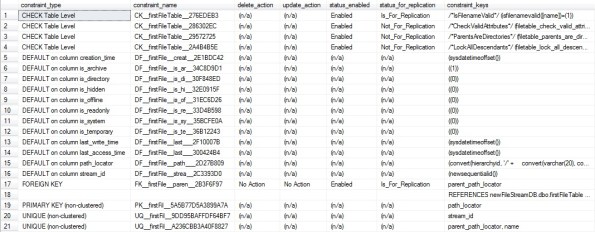
So, what all objects it creates under this new FileTable:
1. The table is created with following predefined Columns:

4. It also creates a FK reference key:

–> Now, when checking under Object Explorer under Tables you won’t see any table (even after refreshing it). But there is a new folder named FileTables, expand it and you can see this table there, shown below:
–> Right click on it and select ‘Explore FileTable Directory’, it will open the folder as shown below:
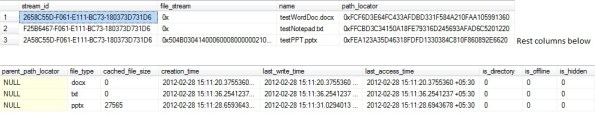
Here, I’ve manually created 3 files, 1 notepad, 1 powerpoint and 1 word doc. You can also copy files from other locations and paste/drop them here. As you paste/drop files here, SQL Server internally updates the [firstFileTable] file table.
–> We can check the table by simply issuing SELECT statement on the table:
SELECT * FROM dbo.firstFileTable
-- Final Cleanup DROP TABLE dbo.firstFileTable GO
I liked this new feature very much as this will ease the work and reduce the overhead of maintaining files with databases.
In my [next post] you can check how you to use Full Text Search with files stored in FileTables.
SQL Server 2012 (DENALI) TSQL – New Feature in SSMS – Surround With
I just stumbled on this new exciting feature of SSMS Denali while trying my hands querying on this new environment.
Here is a scenario: You’ve created a query or a logic with multiple lines of SQL statements. Now you want this to be validated by an IF-ELSE condition or iterate it in a WHILE loop. You will move the cursor to the top and make extra spaces for inserting IF/WHILE {condition} BEGIN, go to the Bottom and terminate the condition/loop with END statement.
But if you are on Denali you won’t have to do this and type anything. Just a few mouse click would do for you, let’s see how:
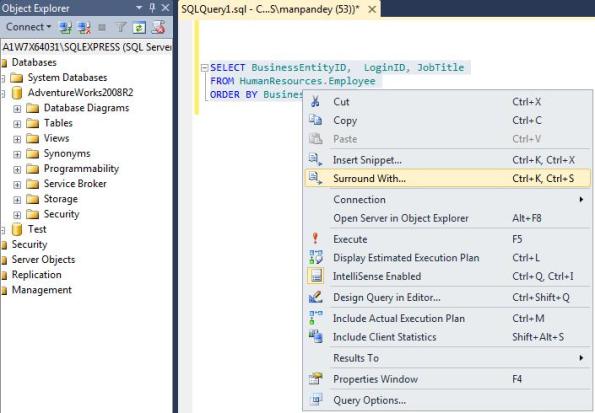
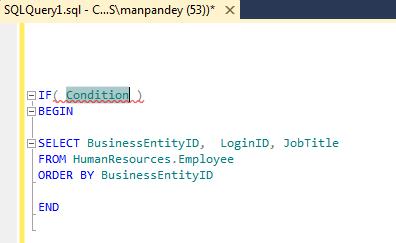
1. Select the SQL statement or logic you want to Surround with, then right click on it, select the “Surround With…” option:
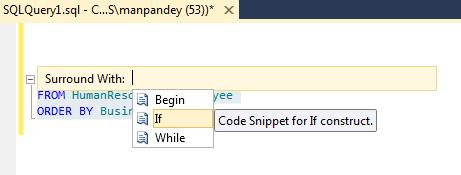
2. Now double click on any 3 of your choice, here I selected the “If” condition:
3. The Editor will automatically write the “IF” syntax for you:
4. You just need to add the condition within brackets as per your requirement.
… nice feature introduced by Microsoft.
SQL Server 2012 (DENALI) TSQL – New feature | OFFSET FETCH Clause (for paging/pagination)
As per MS BOL, the new Denali’s OFFSET-FETCH Clause provides an option to fetch only a window or page of a fix set of results from the result set. OFFSET-FETCH can be used only with the ORDER BY clause.
This was the most awated feature for the frontend/GUI developers to display volumnous data in a small grid, page by page. Prior to this they used to devise not so complex but a bit complex SQL logic to display records page by page. Introduction of this feature has limited the complex logic to a few lines of single SQL statement which is much more optimized.
Let’s see how can we use this feature:
--// Example #1: -- This will skip first 100 records and show next 20 records SELECT BusinessEntityID, LoginID, JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee ORDER BY BusinessEntityID OFFSET 100 ROWS FETCH NEXT 20 ROWS ONLY; GO --// Example #2: -- Start from first record and show next 10 records SELECT BusinessEntityID, LoginID, JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee ORDER BY BusinessEntityID OFFSET 0 ROWS FETCH NEXT 10 ROWS ONLY; -- Skip first 10 records and show next 10 records SELECT BusinessEntityID, LoginID, JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee ORDER BY BusinessEntityID OFFSET 10 ROWS -- To show next page of 10 records, just change the offset by adding the page size, i.e 10. FETCH NEXT 10 ROWS ONLY; GO --// Example #3: -- To use this in front-end, the above logic can be made dynamic by using a few variables, like: DECLARE @StartRec INT DECLARE @PageSize INT DECLARE @RecordEnd INT SET @StartRec = 0 SET @PageSize = 10 SET @RecordEnd = @PageSize WHILE @RecordEnd <> 0 -- I'm using WHILE loop to simulate it here BEGIN SELECT BusinessEntityID, LoginID, JobTitle FROM HumanResources.Employee ORDER BY BusinessEntityID OFFSET @StartRec ROWS FETCH NEXT @PageSize ROWS ONLY SET @RecordEnd = @@ROWCOUNT -- Exit loop at 0 SET @StartRec = @StartRec + @PageSize END GO
Rules to use OFFSET FETCH (via MSDN):
1. ORDER BY is mandatory to use OFFSET and FETCH clause.
2. OFFSET clause is mandatory with FETCH. You can never use, ORDER BY … FETCH.
3. TOP cannot be combined with OFFSET and FETCH in the same query expression.
4. The OFFSET/FETCH rowcount expression can be any arithmetic, constant, or parameter expression that will return an integer value. The rowcount expression does not support scalar sub-queries.
More on MSDN, link: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg699618%28v=sql.110%29.aspx