Archive
New CHOOSE() and IIF() functions introduced in SQL Server 2012 (Denali)
1. The CHOOSE() function provides you array like feature where 1st parameter specifies the index and rest parameters are the array elements, this returns the element at the specified index from a list of elements.
-- CHOOSE() SELECT CHOOSE ( 3, 'Apple', 'Mango', 'Banana', 'Kiwi' ) AS Result; -- Banana SELECT CHOOSE ( 2, 'Manoj', 'Saurabh', 'Andy', 'Dave' ) AS Result; -- Saurabh GO
2. The IIF() function is a good replacement of CASE statement, it returns either of the two values passed to 2nd and 3rd parameter on evaluation of boolean expression to the 1st parameter.
-- IIF() DECLARE @x int = 10; DECLARE @y int = 20; SELECT IIF ( @x > @y, 'TRUE', 'FALSE' ) AS Result; -- FALSE -- CASE equivalent SELECT CASE WHEN @x > @y THEN 'TRUE' ELSE 'FALSE' END AS Result; -- FALSE GO
Note: IIF() function is internally converted to CASE expression by SQL engine and can be nested upto 10 levels like CASE.
–> Video:
“Identity Gap” Issue with the new SEQUENCE feature in SQL Server 2012 … and its workaround
In my previous post I discussed about an issue with IDENTITY property. Here today while working on a similar new feature “SEQUENCE”, I found a similar kind of behavior with it.
Here also when you restart SQL Server or restart the service the last sequence number jumps to a higher random number.
Here is a simple code to reproduce this issue:
-- CREATE a simple Sequence CREATE SEQUENCE CountBy1 START WITH 1 INCREMENT BY 1 MINVALUE 0 NO MAXVALUE ; GO -- CREATE a test table: CREATE TABLE TEST_SEQ (ID INT, NAME VARCHAR(200)); -- INSERT some records: INSERT INTO TEST_SEQ SELECT NEXT VALUE FOR CountBy1, 'Manoj Pandey' INSERT INTO TEST_SEQ SELECT NEXT VALUE FOR CountBy1, 'Gaurav Pandey' GO -- Check the INSERTed records before server restart: SELECT * FROM TEST_SEQ GO -- RESTART SQL Server & INSERT a new record: INSERT INTO TEST_SEQ SELECT NEXT VALUE FOR CountBy1, 'Garvit Pandey' GO -- Check the INSERTed records after server restart: SELECT * FROM TEST_SEQ GO --// Final cleanup DROP TABLE TEST_SEQ DROP SEQUENCE CountBy1
Finally I got the following output:
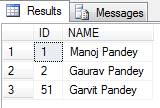
As you can see by running the above test before I restarted SQL Server the SEQUENCE value assigned to the last record was 2, but when I restarted the new SEQUENCE value generated is 51.
Reason: Actually while creating SEQUENCE object SQL Server engine caches the new SEQUENCE values to Increase performance. By default the cache size is 50, so it caches values upto 50 values, and when SQL Server restarts it starts after 50, that’s a bug.
Workaround: To avoid this situation you can put an “NO CACHE” option while declaring the SEQUENCE object, like:
-- CREATE a simple Sequence CREATE SEQUENCE CountBy1 START WITH 1 INCREMENT BY 1 MINVALUE 0 NO MAXVALUE NO CACHE ; -- here GO
This will not cache the future values and you wont get this issue of jumping values and gaps.
To know more about SEQUENCES check my previous blog post, [link].
Jump/Gap Issue with IDENTITY property in SQL Server 2012 … and its workaround (not a bug)
Sometime back there was discussion going on in an SQL Server forum regarding issues with IDENTITY property in the new SQL Server 2012. The issue was that, when restarting SQL Server (or service) the IDENTITY value in a particular table having IDENTITY column jumps to a higher random number and starts from there.
I tried to reproduce this issue, the SQL Server version I’m using is as follows:
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 RC0 - 11.0.1750.32 (X64) Nov 4 2011 17:54:22 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation Business Intelligence Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1)
I reproduced the issue with following code:
-- CREATE a test table:
CREATE TABLE TEST_IDENTITY (
ID INT IDENTITY(1,1),
NAME VARCHAR(200)
);
-- INSERT some records:
INSERT INTO TEST_IDENTITY (NAME)
SELECT 'Manoj Pandey'
INSERT INTO TEST_IDENTITY (NAME)
SELECT 'Gaurav Pandey'
GO
-- Check recently inserted records:
SELECT * FROM TEST_IDENTITY -- 2 records, with ID value 1, 2.
-- Check the current IDENTITY value:
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('TEST_IDENTITY')
--Checking identity information: current identity value '2', current column value '2'.
--DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
GO
-- RESTART SQL Server and check the current IDENTITY value:
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('TEST_IDENTITY')
--Checking identity information: current identity value '11', current column value '2'.
--DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
-- INSERT a new record:
INSERT INTO TEST_IDENTITY (NAME)
SELECT 'Garvit Pandey'
GO
-- Check recently inserted records:
SELECT * FROM TEST_IDENTITY -- 3 records, with ID value 1, 2, 12.
GO
--// Final cleanup
DROP TABLE TEST_IDENTITY
Finally I got the following output:
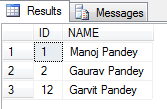
As you can see by running the above test before I restarted SQL Server the IDENTITY value was 2, but when I restarted the IDENTITY value changed to 11.
Thus the new records was inserted with value = 12.
The above bug/issue has been logged in the Microsoft Connect site, [here].
Workaround: Right now there is no fix for this, so you need to check all tables in you database every time your SQL Server restarts and reseed the correct IDENTITY value. Check my blog post to reseed the IDENTITY value.
SQL Server 2012 Upgrade Technical Guide and Why Upgrade
Our SQL Server team have published Customer-ready SQL Server 2012 Upgrade Technical Guide, link.
We encourage customers to upgrade to SQL Server 2012 using this guide (HOW TO UPGRADE), What’s New whitepaper (WHY UPGRADE) created by Joanne Hodgins, and other resources in this web site.
SQL Server 2012 (a.k.a Denali) – New Functions: CONCAT & FORMAT
SQL Server 2012 gem collection has become bigger with the addition of new items with this release. In my previous blog post [link] I’ve discussed about some of these, like:
1. The new CHOOSE() & IFF() logical functions.
2. PARSE(), TRY_CONVERT() & TRY_PARSE() conversion functions.
3. FIRST_VALUE(), LAST_VALUE(), LAG() & LEAD() Analytical functions.
Here I’ll discuss about new String Functions, CONCAT() & FORMAT(). I welcome both of them as they will provide much ease to the developers without depending on various workarounds and considering certain things people normally miss and end up on various goof ups.
–> CONCAT() function: as its name suggests helps combine values of columns into a single string value. Well you can also do this by using “+” operator and combine columns. But what about NULL values and datatype conversion. You can also do it but what if somehow you miss. This function takes care aboout all these things, NULL values and datatype conversion.
Let’s check this:
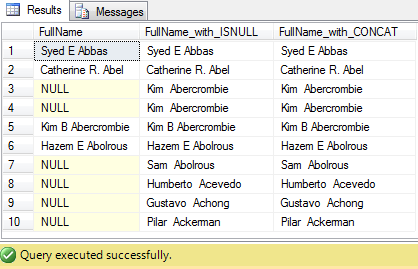
USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO -- Handling NULL implicitly: SELECT TOP 10 -- Combining columns by using + operator (NULL values are not handled): [FirstName] + ' ' + [MiddleName] + ' ' + [LastName] AS 'FullName', -- Combining columns by using + operator by handling NULL values explicitly: ISNULL([FirstName],'') + ' ' + ISNULL([MiddleName],'') + ' ' + ISNULL([LastName],'') AS 'FullName_with_ISNULL', -- Using CONCAT() function (NULL values are implicitly handled): CONCAT([FirstName], ' ', [MiddleName], ' ', [LastName]) AS 'FullName_with_CONCAT' FROM [Person].[Person]
So, the output above lists NULL values when you combine multiple columns with NULL values. The 2nd column lists out expected results as we’ve handled NULL values manually. The 3rd column also results expected results as NULLs are getting handled implicitly by the CONCAT() function.
Now, let’s check how CONCAT() handles Datatype Conversion:
-- Combining columns of different datatypes, gives error: SELECT TOP 10 BusinessEntityID + LastName + EmailPromotion + ModifiedDate AS PersonDetails FROM [Person].[Person]
Error Message: Msg 245, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 Conversion failed when converting the nvarchar value 'Sánchez' to data type int.
-- CONCAT() Handling Datatype conversion implicitly: SELECT TOP 10 CONCAT(BusinessEntityID, LastName, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate) AS PersonDetails FROM [Person].[Person]
Output:-
PersonDetails
1Sánchez0Feb 8 2003 12:00AM
2Duffy1Feb 24 2002 12:00AM
3Tamburello0Dec 5 2001 12:00AM
4Walters0Dec 29 2001 12:00AM
5Erickson0Jan 30 2002 12:00AM
6Goldberg0Feb 17 2002 12:00AM
7Miller2Mar 5 2003 12:00AM
8Margheim0Jan 23 2003 12:00AM
9Matthew0Feb 10 2003 12:00AM
10Raheem2May 28 2003 12:00AM
Check this Video tutorial on FORMAT() function:
–> FORMAT() function: Well I’ve used this function with only dates now and I’m quite happy with it. Now to convert a date to a different format you don’t have to CAST/CONVERT your datetime with lot of different options you don’t memorize or remember. With this new function you can format your dates or datetime values in various formats and in different langauges.
Let’s check this:
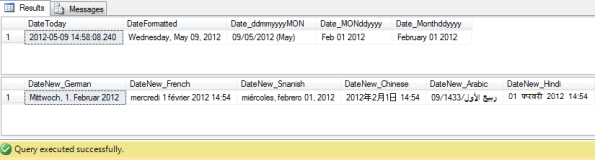
SELECT
GETDATE() AS DateToday,
FORMAT (GETDATE(), 'D') AS DateFormatted,
FORMAT (GETDATE(), 'dd/MM/yyyy (MMM)') AS Date_ddmmyyyyMON,
FORMAT (CAST('2012-02-01' AS DATE), 'MMM dd yyyy') AS Date_MONddyyyy,
FORMAT (CAST('2012-02-01' AS DATE), 'MMMM dd yyyy') AS Date_Monthddyyyy;
DECLARE @someDate DATETIME
SET @someDate = '2012-02-01 14:54:39.300'
SELECT
FORMAT (@someDate, 'D', 'de') AS DateNew_German,
FORMAT (@someDate, 'f', 'fr') AS DateNew_French,
FORMAT (@someDate, 'D', 'es-US') AS DateNew_Snanish,
FORMAT (@someDate, 'f', 'zh') AS DateNew_Chinese,
FORMAT (@someDate, 'D', 'ar') AS DateNew_Arabic,
FORMAT (@someDate, 'f', 'hi-IN') AS DateNew_Hindi;
The 3rd parameter Culture is actaully used to specify the locale and is optional. You can use different Cultures to modify your datetimes in different languages and formats as shown above.
Check this Video tutorial on CONCAT() function: