Archive
SQL DBA – DBID 32767 | Resource Database
select * from sys.databases
On executing the above query it gives me 9 records with DBID ranging from 1 to 9. First 4 DBIDs (1-4) for master, tempdb, model & msdb and another 5 databases (5-9) created by me.
But when I queried some DMVs & DMFs it resulted some records with DBID 32767 which left me clueless until I googled about it. Also submitted a post on my favourite MSDN T-SQL forum and got to know that this ID is reserved for Resource Database. The Resource database is readonly database that does not appear on SSMS and is managed internally by SQL Server engine. More on MS BOL about Resources.
To regenerate this scenario, lets do a simple exercise. Execute the following code (make sure you have AdventureWorks sample database installed):
USE [AdventureWorks] go -- Execute some sample SQL statements select top 10 * from Person.Contact select top 10 * from Production.Product go 10 -- Execute sp_who2 proc sp_who2 go 5
Now execute the query below using sys.dm_exec_query_stats DMV & sys.dm_exec_sql_text(sql_handle) DMF to get the status of what SQL engine is doing behind:
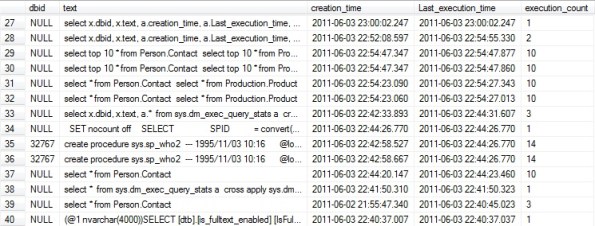
select x.dbid, x.text, a.creation_time, a.Last_execution_time, a.execution_count from sys.dm_exec_query_stats a cross apply sys.dm_exec_sql_text(a.sql_handle) x go
The results displayed in the image above shows 2 records with DBID 32767.
SQL DBA – SQL Queries Executed, Running & Blocking
Here are some TIPS for checking what all SQL statements:
– were executed recently.
– currently running in background.
– blocking or deadlocking.
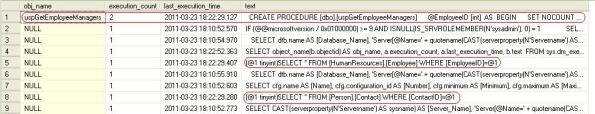
USE [AdventureWorks] GO --// Which SQL query or statement was executed recently? -- Execute the Stored Proc with different parameters & some SQL queries or statements. EXEC uspGetEmployeeManagers 1 GO EXEC uspGetEmployeeManagers 2 GO SELECT * FROM Person.Contact WHERE ContactID = 100 GO SELECT * FROM HumanResources.Employee WHERE EmployeeID = 200 GO -- Following SQL query will get you which SQL statement or Object was executed/used at what time and how many times. SELECT object_name(b.objectid) AS obj_name, a.execution_count, a.last_execution_time, b.text FROM sys.dm_exec_query_stats a CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(a.sql_handle) AS b --where text like '%uspGetEmployeeManagers%' ORDER BY 2 DESC GO
--// Who's executing what SQL statements. sp_who2 GO -- You can check any SPID that is greater than 50. This will give you the SQL statement executing against that SPID. -- Also check if any process is blocking any other process, the BlkBy column will give you the process SPID thats blocking the current process. Put that blocking SPID as paremeter in DBCC INPUTBUFFER() statement and get the SQL statement which has blocked your process. DBCC INPUTBUFFER (51) GO -- You can also Kill the process by providing the blocking SPID as parameter with the KILL statement. KILL 51 GO
More about:
– UDF(TVF) sys.dm_exec_sql_text
– View sys.dm_exec_query_stats
SQL DBA – When was the Table, View, Stored Procedure Created or Modified
On my previous blog posts [link] I discussed about System Catalog views and some tips to get the informaion regarding Database objects, like: Tables, Views, etc.
Adding to that post, this post provides the basic information that various DBAs & Developers are interested in, i.e. when was the Table created? or When was that particular Stored Procedure modified or updated?
Following set of queries provides this information:
select object_id, name, create_date, type_desc, modify_date from sys.tables UNION select object_id, name, create_date, type_desc, modify_date from sys.views UNION select object_id, name, create_date, type_desc, modify_date from sys.procedures UNION select object_id, name, create_date, type_desc, modify_date from sys.triggers
-OR- a single query to check all objects information:
select object_id, name, create_date, type_desc, modify_date
from sys.all_objects
where type in ('U', 'V', 'P', 'TR' ,'FN', 'IF', 'TF')
order by type, name
By querying the sys.all_objects view you can also get the information about other DB objects other than listed above, like: Indexes, Constraints, Synonyms, Stats, etc.
MS BOL link on sysobjects and object-type codes: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms177596.aspx
SQL DBA – Querying SQL Server Metadata, INFORMATION_SCHEMA, sysObjects, System Catalog, etc
While writing complex code & business logic in my scrits & stored-procdedures most of the time I wonder…
– What table does a particular column belongs to?
– What all Stored Procedures effect a particular table?
– How can I see what particular constraint does my tables have?
– What all Foreign Keys defined in table’s columns are linked to?
These and many more questions can be answered by querying the SQL Server System Catalog and metadata that SQL Server manages very beautifully.
The SQL Server system catalogs is a set of views that show metadata that describes the objects in an instance of SQL Server. Metadata is data that describes the attributes of objects in a system. SQL Server-based applications can access the information in the system catalogs by using some of the following:
-> Information Schema, views to quickly retrieve metadata
-> Catalog Views, recommened by MS.
–// Information Schema Views: They present the catalog information in a format that is independent of any catalog table implementation and therefore are not affected by changes in the underlying catalog tables.
-- INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
TABLE_CATALOG TABLE_SCHEMA TABLE_NAME TABLE_TYPE
AdventureWorks Production ProductProductPhoto BASE TABLE
AdventureWorks Sales StoreContact BASE TABLE
AdventureWorks Person Address BASE TABLE
AdventureWorks Production ProductReview BASE TABLE
AdventureWorks Production TransactionHistory BASE TABLE
AdventureWorks Person AddressType BASE TABLE
select distinct TABLE_SCHEMA from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
TABLE_SCHEMA
dbo
HumanResources
Person
Production
Purchasing
Sales
select distinct TABLE_TYPE from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
TABLE_TYPE
BASE TABLE
VIEW
-- INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS select TABLE_CATALOG, TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME, COLUMN_NAME, DATA_TYPE, CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH, CHARACTER_OCTET_LENGTH, NUMERIC_PRECISION, NUMERIC_PRECISION_RADIX, NUMERIC_SCALE from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where COLUMN_NAME = 'ContactID' -- INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEWS select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEW_TABLE_USAGE select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.VIEW_COLUMN_USAGE -- INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES select distinct ROUTINE_SCHEMA from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES
ROUTINE_SCHEMA
dbo
HumanResources
select distinct ROUTINE_TYPE from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES
ROUTINE_TYPE
FUNCTION
PROCEDURE
select ROUTINE_SCHEMA, ROUTINE_NAME, ROUTINE_TYPE, DATA_TYPE, ROUTINE_BODY, ROUTINE_DEFINITION, IS_DETERMINISTIC, SQL_DATA_ACCESS, CREATED, LAST_ALTERED from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES where ROUTINE_DEFINITION like '%ContactID%' select * from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINE_COLUMNS
–// Catalog Views: provide access to metadata that is stored in every database on the server.
-- The following SQL statement will pull all Stored-Procedures & Functions in the Database.
select c.id, object_name(c.id) as obj_name_c, o.name as obj_name_o, o.xtype, c.text, o.crdate, o.refdate
from sys.syscomments c
join sys.sysobjects o
on o.id = c.id
where xtype in ('P', 'FN')
-- This following SQL statement will pull all Objects information with in the Database.
select c.id, object_name(c.id) as obj_name_c, -- o.name
case xtype
when 'C' then 'Check Constraint'
when 'D' then 'Default Constraint'
when 'F' then 'Foreign Key Constraint'
when 'L' then 'Log'
when 'P' then 'Stored Procedure'
when 'PK' then 'Primary Key Constraint'
when 'RF' then 'Replication Filter Procedure'
when 'S' then 'System Table'
when 'TR' then 'Trigger'
when 'U' then 'User Table'
when 'UQ' then 'Unique Constraint'
when 'V' then 'View'
when 'X' then 'Extended Procedure'
when 'FN' then 'User Defined Function'
else 'N/A'
end as obj_type,
c.text, o.crdate, o.refdate
from sys.syscomments c
join sys.sysobjects o
on o.id = c.id
-- Pulls Foreign Key and its links
select fk.name as fk_name, fk.object_id, object_name(fk.parent_object_id) as table_name,
col_name(fc.parent_object_id, fc.parent_column_id) as constraint_col_name,
object_name(fk.referenced_object_id) as referenced_table,
COL_NAME(fc.referenced_object_id, fc.referenced_column_id) AS referenced_col_name,
fk.delete_referential_action_desc
from sys.foreign_keys fk
join sys.foreign_key_columns fc
on fk.object_id = fc.constraint_object_id
Note: All examples are executed on SQL Server 2005 AdventureWorks DB.
More info from MSDN BOL: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms189082(v=SQL.90).aspx
MSDN FAQs: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms345522.aspx
SQL DBA – Database Mail Setup – SQL Server 2005
Database Mail, a new addition to the SQL Server 2005 database engine, is an enterprise solution for sending e-mail messages from the Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Database Engine. Using Database Mail, your database applications can send e-mail messages to users. The messages can contain query results, and can also include files from any resource on your network. Database Mail is designed for reliability, scalability, security, and supportability.
Database Mail provides a robust, high-performance replacement for the most commonly requested features of SQL Mail. Database Mail is designed to operate with SMTP servers, and is tested with Microsoft SMTP servers.
Note: Database Mail is not active by default. To use Database Mail, you must explicitly enable Database Mail by using either the “SQL Server Surface Area Configuration” tool or the “Database Mail Configuration Wizard“.
Database Mail Setup:
Enabling the Database Mail feature: By default the Database mail Stored-Procs are disabled.
For Express Edition, check the required files exists in MSSQL\Binn folder. If not then copy the following 3 files:
1. DatabaseMail90.exe
2. DatabaseMailEngine.dll
3. DatabaseMailProtocols.dll
Then execute the following Stored-Porcs:
exec dbo.sysmail_start_sp exec dbo.sysmail_stop_sp
A User must be a member of the DatabaseMailUserRole database role in the msdb database.
To Enable Database Mail execute the following block of code:
use master go exec sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1 reconfigure exec sp_configure 'Database Mail XPs', 1 reconfigure
Initial Cleanup:
IF EXISTS(
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_profileaccount pa
JOIN msdb.dbo.sysmail_profile p ON pa.profile_id = p.profile_id
JOIN msdb.dbo.sysmail_account a ON pa.account_id = a.account_id
WHERE
p.name = @ProfileName AND
a.name = @AccountName)
BEGIN
PRINT 'Deleting Profile Account'
EXECUTE sysmail_delete_profileaccount_sp
@profile_name = @ProfileName,
@account_name = @AccountName
END
IF EXISTS(
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_profile p
WHERE p.name = @ProfileName)
BEGIN
PRINT 'Deleting Profile.'
EXECUTE sysmail_delete_profile_sp
@profile_name = @ProfileName
END
IF EXISTS(
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_account a
WHERE a.name = @AccountName)
BEGIN
PRINT 'Deleting Account.'
EXECUTE sysmail_delete_account_sp
@account_name = @AccountName
END
Setting up Accounts & Profiles for DB Mail:
Create a Database Mail account for holding information about an SMTP account.
An Account holds information for only one e-mail server, such as the account name, e-mail address, reply-to e-mail address, server name or IP address, and some optional security settings.
--// Create a Database Mail account
EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_account_sp
@account_name = 'Test Mail Account',
@description = 'Mail account for administrative e-mail.',
@email_address = 'abc@xyz.com',
@replyto_address = 'abc@xyz.com',
@display_name = 'Manoj Pandey',
@mailserver_name = 'smtp.xxxx.net',
@port = 587,
@username = 'xyz',
@password = 'xxyyzz',
@enable_ssl = 1
-- Create a Database Mail profile
EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profile_sp
@profile_name = 'Test Mail Profile',
@description = 'Profile used for administrative mail.'
-- Add the account to the profile
EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_profileaccount_sp
@profile_name = 'Test Mail Profile',
@account_name = 'Test Mail Account',
@sequence_number =1
-- Grant access to the profile to the DBMailUsers role
EXECUTE msdb.dbo.sysmail_add_principalprofile_sp
@profile_name = 'Test Mail Profile',
@principal_name = 'public',
@is_default = 1
Sending Mail and Check its status:
--Send mail
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@recipients=N'manub22@gmail.com',
@body= 'Test Email Body',
@subject = 'Test Email Subject',
@profile_name = 'Test Mail Profile'
--Send mail with attachment
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail
@profile_name = 'DBMail'
,@recipients = 'GroupSQLDBA@MyCo.com'
,@from_address = 'DBMail@MyCo.com'
,@query = 'SELECT resource_type, resource_database_id,
request_mode, request_session_id
FROM sys.dm_tran_locks
WHERE request_mode IN (''IX'', ''X'')'
,@subject = 'Exclusive Locks'
,@attach_query_result_as_file = 1 ;
Important Tables used in configuring Database mail and check their status:
--Profiles
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_profile
--Accounts
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_account
--Profile Accounts
select * from msdb.dbo.sysmail_profileaccount
--Principal Profile
select * from msdb.dbo.sysmail_principalprofile
--Mail Server
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_server
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_servertype
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_configuration
--Email Sent Status
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_allitems
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_sentitems
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_unsentitems
SELECT * FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_faileditems
--Email Status
SELECT SUBSTRING(fail.subject,1,25) AS 'Subject',
fail.mailitem_id,
LOG.description
FROM msdb.dbo.sysmail_event_log LOG
join msdb.dbo.sysmail_faileditems fail
ON fail.mailitem_id = LOG.mailitem_id
WHERE event_type = 'error'
--Mail Queues
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_help_queue_sp
--DB Mail Status
EXEC msdb.dbo.sysmail_help_status_sp
Note: After performing above steps the mails were not getting sent. I was configuring DB mail from my client machine, even with the admin account. I was getting various errors like:
The mail could not be sent to the recipients because of the mail server failure. (Sending Mail using Account 19 (2010-10-22T07:24:21). Exception Message: Could not connect to mail server. (A connection attempt failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time, or established connection failed because connected host has failed to respond IP_ADD:25).
Then I tried to setup the DB mail from the server itself and it worked in one go.