Archive
View Dependencies of a Table from SSMS and T-SQL script used internally by SSMS
Here we will see how to check the Table level dependencies, means what all Database Objects a Table is related to, like Views, Stored Procedures (SPs), Functions (UDFs), Triggers, etc.
Go to Object Explorer, and expand the Databases -> Tables and Right click on the Table that you want to see dependencies.
Select View Dependencies, you will get a popup listing all objects that depends upon this table.
–>1. The below image shows the Objects that depend on Customer table:

–>2. Once you select the second radio-button it shows the Objects on which Customer table depends:

–> And here is a very lengthy (~900 lines) T-SQL Code that I generated from SSMS & SQL Profiler to check the same Dependencies of a Table in SQL Server 2014. You can also create a Stored Procedure and apply the Table & Schema as parameters.
You can just replace the Table & Schema in the first 2 lines and execute the code to check table dependencies:
DECLARE @Table_name NVARCHAR(1000) = N'Customer' -- replace your table here
DECLARE @Schema_name NVARCHAR(1000) = N'Sales' -- replace the schema here
CREATE TABLE #tempdep (objid int NOT NULL, objname sysname NOT NULL, objschema sysname NULL, objdb sysname NOT NULL, objtype smallint NOT NULL)
BEGIN TRANSACTION
exec sp_executesql N'INSERT INTO #tempdep
SELECT
tbl.object_id AS [ID],
tbl.name AS [Name],
SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id) AS [Schema],
db_name(),
3
FROM
sys.tables AS tbl
WHERE
(tbl.name=@_msparam_0 and SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id)=@_msparam_1)',N'@_msparam_0 nvarchar(4000),@_msparam_1 nvarchar(4000)',@_msparam_0=@Table_name,@_msparam_1=@Schema_name
COMMIT TRANSACTION
declare @find_referencing_objects int
set @find_referencing_objects = 1 -- Objects that depend on Customer table
--set @find_referencing_objects = 0 -- Objects on which Customer table depends
-- parameters:
-- 1. create table #tempdep (objid int NOT NULL, objtype smallint NOT NULL)
-- contains source objects
-- 2. @find_referencing_objects defines ordering
-- 1 order for drop
-- 0 order for script
declare @must_set_nocount_off bit
set @must_set_nocount_off = 0
IF @@OPTIONS & 512 = 0
set @must_set_nocount_off = 1
set nocount on
declare @u int
declare @udf int
declare @v int
declare @sp int
declare @def int
declare @rule int
declare @tr int
declare @uda int
declare @uddt int
declare @xml int
declare @udt int
declare @assm int
declare @part_sch int
declare @part_func int
declare @synonym int
declare @sequence int
declare @udtt int
declare @ddltr int
declare @unknown int
declare @pg int
set @u = 3
set @udf = 0
set @v = 2
set @sp = 4
set @def = 6
set @rule = 7
set @tr = 8
set @uda = 11
set @synonym = 12
set @sequence = 13
--above 100 -> not in sys.objects
set @uddt = 101
set @xml = 102
set @udt = 103
set @assm = 1000
set @part_sch = 201
set @part_func = 202
set @udtt = 104
set @ddltr = 203
set @unknown = 1001
set @pg = 204
-- variables for referenced type obtained from sys.sql_expression_dependencies
declare @obj int
set @obj = 20
declare @type int
set @type = 21
-- variables for xml and part_func are already there
create table #t1
(
object_id int NULL,
object_name sysname collate database_default NULL,
object_schema sysname collate database_default NULL,
object_db sysname NULL,
object_svr sysname NULL,
object_type smallint NOT NULL,
relative_id int NOT NULL,
relative_name sysname collate database_default NOT NULL,
relative_schema sysname collate database_default NULL,
relative_db sysname NULL,
relative_svr sysname NULL,
relative_type smallint NOT NULL,
schema_bound bit NOT NULL,
rank smallint NULL,
degree int NULL
)
-- we need to create another temporary table to store the dependencies from sys.sql_expression_dependencies till the updated values are inserted finally into #t1
create table #t2
(
object_id int NULL,
object_name sysname collate database_default NULL,
object_schema sysname collate database_default NULL,
object_db sysname NULL,
object_svr sysname NULL,
object_type smallint NOT NULL,
relative_id int NOT NULL,
relative_name sysname collate database_default NOT NULL,
relative_schema sysname collate database_default NULL,
relative_db sysname NULL,
relative_svr sysname NULL,
relative_type smallint NOT NULL,
schema_bound bit NOT NULL,
rank smallint NULL
)
-- This index will ensure that we have unique parent-child relationship
create unique clustered index i1 on #t1(object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, object_type, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_type) with IGNORE_DUP_KEY
declare @iter_no int
set @iter_no = 1
declare @rows int
set @rows = 1
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select l.objid, l.objname, l.objschema, l.objdb, l.objtype, l.objid, l.objname, l.objschema, l.objdb, l.objtype, 1, @iter_no from #tempdep l
-- change the object_id of table types to their user_defined_id
update #t1 set object_id = tt.user_type_id, relative_id = tt.user_type_id
from sys.table_types as tt where tt.type_table_object_id = #t1.object_id and object_type = @udtt
while @rows > 0
begin
set @rows = 0
if (1 = @find_referencing_objects)
begin
-- HARD DEPENDENCIES
-- these dependencies have to be in the same database only
-- tables that reference uddts or udts
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tbl.object_id, tbl.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id), t.object_db, @u, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as c on c.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.tables as tbl on tbl.object_id = c.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and (t.object_type = @uddt OR t.object_type = @udt) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- udtts that reference uddts or udts
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tt.user_type_id, tt.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tt.schema_id), t.object_db, @udtt, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as c on c.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.table_types as tt on tt.type_table_object_id = c.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and (t.object_type = @uddt OR t.object_type = @udt) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- tables/views that reference triggers
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @tr, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.objects as o on o.parent_object_id = t.object_id and o.type = 'TR'
where @iter_no = t.rank and (t.object_type = @u OR t.object_type = @v) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- tables that reference defaults (only default objects)
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @u, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as clmns on clmns.default_object_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = clmns.object_id and 0 = isnull(o.parent_object_id, 0)
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @def and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- types that reference defaults (only default objects)
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tp.user_type_id, tp.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tp.schema_id), t.object_db, @uddt, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.types as tp on tp.default_object_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = t.object_id and 0 = isnull(o.parent_object_id, 0)
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @def and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- tables that reference rules
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tbl.object_id, tbl.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id), t.object_db, @u, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as clmns on clmns.rule_object_id = t.object_id
join sys.tables as tbl on tbl.object_id = clmns.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.relative_type = @rule and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- types that reference rules
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tp.user_type_id, tp.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tp.schema_id), t.object_db, @uddt, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.types as tp on tp.rule_object_id = t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @rule and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- tables that reference XmlSchemaCollections
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tbl.object_id, tbl.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id), t.object_db, @u, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as c on c.xml_collection_id = t.object_id
join sys.tables as tbl on tbl.object_id = c.object_id -- eliminate views
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @xml and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- table types that reference XmlSchemaCollections
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tt.user_type_id, tt.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tt.schema_id), t.object_db, @udtt, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as c on c.xml_collection_id = t.object_id
join sys.table_types as tt on tt.type_table_object_id = c.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @xml and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- procedures that reference XmlSchemaCollections
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, (case when o.type in ( 'P', 'RF', 'PC') then @sp else @udf end), t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.parameters as c on c.xml_collection_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = c.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @xml and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- udf, sp, uda, trigger all that reference assembly
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, (case o.type when 'AF' then @uda when 'PC' then @sp when 'FS' then @udf when 'FT' then @udf when 'TA' then @tr else @udf end), t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.assembly_modules as am on ((am.assembly_id = t.object_id) and (am.assembly_id >= 65536))
join sys.objects as o on am.object_id = o.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @assm and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- udt that reference assembly
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select at.user_type_id, at.name, SCHEMA_NAME(at.schema_id), t.object_db, @udt, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.assembly_types as at on ((at.assembly_id = t.object_id) and (at.is_user_defined = 1))
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @assm and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- assembly that reference assembly
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select asm.assembly_id, asm.name, t.object_db, @assm, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.assembly_references as ar on ((ar.referenced_assembly_id = t.object_id) and (ar.referenced_assembly_id >= 65536))
join sys.assemblies as asm on asm.assembly_id = ar.assembly_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @assm and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- table references table
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tbl.object_id, tbl.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id), t.object_db, @u, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.foreign_keys as fk on fk.referenced_object_id = t.object_id
join sys.tables as tbl on tbl.object_id = fk.parent_object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @u and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- uda references types
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @uda, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.parameters as p on p.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = p.object_id and o.type = 'AF'
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type in (@udt, @uddt, @udtt) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
-- table,view references partition scheme
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, (case o.type when 'V' then @v else @u end), t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.indexes as idx on idx.data_space_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = idx.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @part_sch and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- partition scheme references partition function
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select ps.data_space_id, ps.name, t.object_db, @part_sch, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.partition_schemes as ps on ps.function_id = t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @part_func and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- plan guide references sp, udf, triggers
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select pg.plan_guide_id, pg.name, t.object_db, @pg, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.plan_guides as pg on pg.scope_object_id = t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type in (@sp, @udf, @tr) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- synonym refrences object
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select s.object_id, s.name, SCHEMA_NAME(s.schema_id), t.object_db, @synonym, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 0, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.synonyms as s on object_id(s.base_object_name) = t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- sequences that reference uddts
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select s.object_id, s.name, SCHEMA_NAME(s.schema_id), t.object_db, @sequence, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 0, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.sequences as s on s.user_type_id = t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and (t.object_type = @uddt) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- SOFT DEPENDENCIES
DECLARE name_cursor CURSOR
FOR
SELECT DISTINCT t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_type
FROM #t1 as t
WHERE @iter_no = t.rank and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name()) and t.object_type NOT IN (@part_sch, @assm, @tr, @ddltr)
OPEN name_cursor
DECLARE @objid int
DECLARE @objname sysname
DECLARE @objschema sysname
DECLARE @objtype smallint
DECLARE @fullname sysname
DECLARE @objecttype sysname
FETCH NEXT FROM name_cursor INTO @objid, @objname, @objschema, @objtype
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS <> -1)
BEGIN
SET @fullname = case when @objschema IS NULL then quotename(@objname)
else quotename(@objschema) + '.' + quotename(@objname) end
SET @objecttype = case when @objtype in (@uddt, @udt, @udtt) then 'TYPE'
when @objtype = @xml then 'XML_SCHEMA_COLLECTION'
when @objtype = @part_func then 'PARTITION_FUNCTION'
else 'OBJECT' end
insert #t2 (object_type, object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select
case dep.referencing_class when 1 then (select
case when obj.type = 'U' then @u
when obj.type = 'V' then @v
when obj.type = 'TR' then @tr
when obj.type in ('P', 'RF', 'PC') then @sp
when obj.type in ('AF') then @uda
when obj.type in ('TF', 'FN', 'IF', 'FS', 'FT') then @udf
when obj.type = 'D' then @def
when obj.type = 'SN' then @synonym
when obj.type = 'SO' then @sequence
else @obj
end
from sys.objects as obj where obj.object_id = dep.referencing_id)
when 6 then (select
case when (tp.is_assembly_type = 1) then @udt
when (tp.is_table_type = 1) then @udtt
else @uddt
end
from sys.types as tp where tp.user_type_id = dep.referencing_id)
when 7 then @u
when 9 then @u
when 10 then @xml
when 12 then @ddltr
when 21 then @part_func
end,
dep.referencing_id,
dep.referencing_entity_name,
dep.referencing_schema_name,
db_name(), null,
@objid, @objname,
@objschema, db_name(), @objtype,
0, @iter_no + 1
from sys.dm_sql_referencing_entities(@fullname, @objecttype) dep
FETCH NEXT FROM name_cursor INTO @objid, @objname, @objschema, @objtype
END
CLOSE name_cursor
DEALLOCATE name_cursor
update #t2 set object_id = obj.object_id, object_name = obj.name, object_schema = schema_name(obj.schema_id), object_type = case when obj.type = 'U' then @u when obj.type = 'V' then @v end
from sys.objects as o
join sys.objects as obj on obj.object_id = o.parent_object_id
where o.object_id = #t2.object_id and (#t2.object_type = @obj OR o.parent_object_id != 0) and #t2.rank = @iter_no + 1
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_svr, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_svr, relative_type, schema_bound, rank
from #t2 where @iter_no + 1 = rank and #t2.object_id != #t2.relative_id
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
end
else
begin
-- SOFT DEPENDENCIES
-- insert all values from sys.sql_expression_dependencies for the corresponding object
-- first insert them in #t2, update them and then finally insert them in #t1
insert #t2 (object_type, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select
case dep.referenced_class when 1 then @obj
when 6 then @type
when 7 then @u
when 9 then @u
when 10 then @xml
when 21 then @part_func
end,
dep.referenced_entity_name,
dep.referenced_schema_name,
dep.referenced_database_name,
dep.referenced_server_name,
t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type,
dep.is_schema_bound_reference, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.sql_expression_dependencies as dep on dep.referencing_id = t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_svr IS NULL and t.object_db = db_name()
-- insert all the dependency values in case of a table that references a check
insert #t2 (object_type, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select
case dep.referenced_class when 1 then @obj
when 6 then @type
when 7 then @u
when 9 then @u
when 10 then @xml
when 21 then @part_func
end,
dep.referenced_entity_name,
dep.referenced_schema_name,
dep.referenced_database_name,
dep.referenced_server_name,
t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type,
dep.is_schema_bound_reference, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.sql_expression_dependencies as d on d.referenced_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = d.referencing_id and o.type = 'C'
join sys.sql_expression_dependencies as dep on dep.referencing_id = d.referencing_id and dep.referenced_id != t.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_svr IS NULL and t.object_db = db_name() and t.object_type = @u
-- insert all the dependency values in case of an object that belongs to another object whose dependencies are being found
insert #t2 (object_type, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select
case dep.referenced_class when 1 then @obj
when 6 then @type
when 7 then @u
when 9 then @u
when 10 then @xml
when 21 then @part_func
end,
dep.referenced_entity_name,
dep.referenced_schema_name,
dep.referenced_database_name,
dep.referenced_server_name,
t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type,
dep.is_schema_bound_reference, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.objects as o on o.parent_object_id = t.object_id
join sys.sql_expression_dependencies as dep on dep.referencing_id = o.object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_svr IS NULL and t.object_db = db_name()
-- queries for objects with object_id null and object_svr null - resolve them
-- we will build the query to resolve the objects
-- increase @rows as we bind the objects
DECLARE db_cursor CURSOR
FOR
select distinct ISNULL(object_db, db_name()) from #t2 as t
where t.rank = (@iter_no+1) and t.object_id IS NULL and t.object_svr IS NULL
OPEN db_cursor
DECLARE @dbname sysname
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @dbname
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS <> -1)
BEGIN
IF (db_id(@dbname) IS NULL)
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @dbname
CONTINUE
END
DECLARE @query nvarchar(MAX)
-- when schema is not null
-- @obj
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = obj.object_id, object_type =
case when obj.type = ''U'' then ' + CAST(@u AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''V'' then ' + CAST(@v AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''TR'' then ' + CAST(@tr AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''P'', ''RF'', ''PC'' ) then ' + CAST(@sp AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''AF'' ) then ' + CAST(@uda AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''TF'', ''FN'', ''IF'', ''FS'', ''FT'' ) then ' + CAST(@udf AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''D'' then ' + CAST(@def AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''SN'' then ' + CAST(@synonym AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''SO'' then ' + CAST(@sequence AS nvarchar(8)) +
' else ' + CAST(@unknown AS nvarchar(8)) +
' end
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.objects as obj
join ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = obj.schema_id
where obj.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and sch.name = #t2.object_schema collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@obj AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NOT NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @type
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = t.user_type_id, object_type = case when t.is_assembly_type = 1 then ' + CAST(@udt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' when t.is_table_type = 1 then ' + CAST(@udtt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' else ' + CAST(@uddt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' end
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.types as t
join ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = t.schema_id
where t.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and sch.name = #t2.object_schema collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@type AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NOT NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @xml
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = x.xml_collection_id
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.xml_schema_collections as x
join ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = x.schema_id
where x.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and sch.name = #t2.object_schema collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@xml AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NOT NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @part_func - schema is always null
-- @schema is null
-- consider schema as 'dbo'
-- @obj
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = obj.object_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(obj.schema_id), object_type =
case when obj.type = ''U'' then ' + CAST(@u AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''V'' then ' + CAST(@v AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''TR'' then ' + CAST(@tr AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''P'', ''RF'', ''PC'' ) then ' + CAST(@sp AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''AF'' ) then ' + CAST(@uda AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''TF'', ''FN'', ''IF'', ''FS'', ''FT'' ) then ' + CAST(@udf AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''D'' then ' + CAST(@def AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''SN'' then ' + CAST(@synonym AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''SO'' then ' + CAST(@sequence AS nvarchar(8)) +
' else ' + CAST(@unknown AS nvarchar(8)) +
' end
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.objects as obj
where obj.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and SCHEMA_NAME(obj.schema_id) = ''dbo''
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@obj AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @type
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = t.user_type_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(t.schema_id), object_type = case when t.is_assembly_type = 1 then ' + CAST(@udt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' when t.is_table_type = 1 then ' + CAST(@udtt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' else ' + CAST(@uddt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' end
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.types as t
where t.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and SCHEMA_NAME(t.schema_id) = ''dbo''
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@type AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @xml
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = x.xml_collection_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(x.schema_id)
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.xml_schema_collections as x
where x.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and SCHEMA_NAME(x.schema_id) = ''dbo''
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@xml AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- consider schema as t.relative_schema
-- the parent object will have the default schema of user in case of dynamic schema binding
-- @obj
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = obj.object_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(obj.schema_id), object_type =
case when obj.type = ''U'' then ' + CAST(@u AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''V'' then ' + CAST(@v AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''TR'' then ' + CAST(@tr AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''P'', ''RF'', ''PC'' ) then ' + CAST(@sp AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''AF'' ) then ' + CAST(@uda AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type in ( ''TF'', ''FN'', ''IF'', ''FS'', ''FT'' ) then ' + CAST(@udf AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''D'' then ' + CAST(@def AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''SN'' then ' + CAST(@synonym AS nvarchar(8)) +
' when obj.type = ''SO'' then ' + CAST(@sequence AS nvarchar(8)) +
' else ' + CAST(@unknown AS nvarchar(8)) +
' end
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.objects as obj
join ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = obj.schema_id
where obj.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and sch.name = #t2.relative_schema collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@obj AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @type
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = t.user_type_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(t.schema_id), object_type = case when t.is_assembly_type = 1 then ' + CAST(@udt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' when t.is_table_type = 1 then ' + CAST(@udtt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' else ' + CAST(@uddt AS nvarchar(8)) + ' end
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.types as t
join ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = t.schema_id
where t.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and sch.name = #t2.relative_schema collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@type AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @xml
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = x.xml_collection_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(x.schema_id)
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.xml_schema_collections as x
join ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = x.schema_id
where x.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and sch.name = #t2.relative_schema collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@xml AS nvarchar(8)) + ' and #t2.object_schema IS NULL
and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- @part_func always have schema as null
SET @query = 'update #t2 set object_db = N' + quotename(@dbname, '''') + ', object_id = p.function_id
from ' + quotename(@dbname) + '.sys.partition_functions as p
where p.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default
and #t2.object_type = ' + CAST(@part_func AS nvarchar(8)) +
' and (#t2.object_db IS NULL or #t2.object_db = ''' + @dbname + ''')
and #t2.rank = (' + CAST(@iter_no AS nvarchar(8)) + '+1) and #t2.object_id IS NULL and #t2.object_svr IS NULL'
EXEC (@query)
-- update the shared object if any (schema is not null)
update #t2 set object_db = 'master', object_id = o.object_id, object_type = @sp
from master.sys.objects as o
join master.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = o.schema_id
where o.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default and sch.name = #t2.object_schema collate database_default and
o.type in ('P', 'RF', 'PC') and #t2.object_id IS null and
#t2.object_name LIKE 'sp/_%' ESCAPE '/' and #t2.object_db IS null and #t2.object_svr IS null
-- update the shared object if any (schema is null)
update #t2 set object_db = 'master', object_id = o.object_id, object_schema = SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), object_type = @sp
from master.sys.objects as o
where o.name = #t2.object_name collate database_default and SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id) = 'dbo' collate database_default and
o.type in ('P', 'RF', 'PC') and
#t2.object_schema IS null and #t2.object_id IS null and
#t2.object_name LIKE 'sp/_%' ESCAPE '/' and #t2.object_db IS null and #t2.object_svr IS null
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @dbname
END
CLOSE db_cursor
DEALLOCATE db_cursor
update #t2 set object_type = @unknown where object_id IS NULL
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_svr, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_svr, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_svr, relative_type, schema_bound, rank
from #t2 where @iter_no + 1 = rank
SET @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- HARD DEPENDENCIES
-- uddt or udt referenced by table
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tp.user_type_id, tp.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tp.schema_id), t.object_db, case tp.is_assembly_type when 1 then @udt else @uddt end, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as col on col.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.types as tp on tp.user_type_id = col.user_type_id and tp.schema_id != 4
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @u and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- uddt or udt referenced by table type
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tp.user_type_id, tp.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tp.schema_id), t.object_db, case tp.is_assembly_type when 1 then @udt else @uddt end, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.table_types as tt on tt.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.columns as col on col.object_id = tt.type_table_object_id
join sys.types as tp on tp.user_type_id = col.user_type_id and tp.schema_id != 4
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @udtt and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- table or view referenced by trigger
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, case o.type when 'V' then @v else @u end, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.triggers as tr on tr.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = tr.parent_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @tr and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- defaults (only default objects) referenced by tables
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @def, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as clmns on clmns.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = clmns.default_object_id and 0 = isnull(o.parent_object_id, 0)
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @u and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- defaults (only default objects) referenced by types
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @def, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.types as tp on tp.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = tp.default_object_id and 0 = isnull(o.parent_object_id, 0)
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @uddt and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- rules referenced by tables
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @rule, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as clmns on clmns.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = clmns.rule_object_id and 0 = isnull(o.parent_object_id, 0)
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.relative_type = @u and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- rules referenced by types
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, @rule, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.types as tp on tp.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = tp.rule_object_id and 0 = isnull(o.parent_object_id, 0)
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.relative_type = @uddt and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- XmlSchemaCollections referenced by tables
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select x.xml_collection_id, x.name, SCHEMA_NAME(x.schema_id), t.object_db, @xml, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.columns as c on c.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.xml_schema_collections as x on x.xml_collection_id = c.xml_collection_id and x.schema_id != 4
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @u and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- XmlSchemaCollections referenced by tabletypes
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select x.xml_collection_id, x.name, SCHEMA_NAME(x.schema_id), t.object_db, @xml, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.table_types as tt on tt.user_type_id = t.object_id
join sys.columns as c on c.object_id = tt.type_table_object_id
join sys.xml_schema_collections as x on x.xml_collection_id = c.xml_collection_id and x.schema_id != 4
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @udtt and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- XmlSchemaCollections referenced by procedures
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select x.xml_collection_id, x.name, SCHEMA_NAME(x.schema_id), t.object_db, @xml, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.parameters as c on c.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.xml_schema_collections as x on x.xml_collection_id = c.xml_collection_id and x.schema_id != 4
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type in (@sp, @udf) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- table referenced by table
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tbl.object_id, tbl.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tbl.schema_id), t.object_db, @u, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.foreign_keys as fk on fk.parent_object_id = t.object_id
join sys.tables as tbl on tbl.object_id = fk.referenced_object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @u and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- uddts referenced by uda
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tp.user_type_id, tp.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tp.schema_id), t.object_db, case when tp.is_table_type = 1 then @udtt when tp.is_assembly_type = 1 then @udt else @uddt end, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.parameters as p on p.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.types as tp on tp.user_type_id = p.user_type_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @uda and t.object_type = @uda and tp.user_type_id>256
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- assembly referenced by assembly
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select asm.assembly_id, asm.name, t.object_db, @assm, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.assembly_references as ar on ((ar.assembly_id = t.object_id) and (ar.referenced_assembly_id >= 65536))
join sys.assemblies as asm on asm.assembly_id = ar.referenced_assembly_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @assm and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- assembly referenced by udt
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select asm.assembly_id, asm.name, t.object_db, @assm, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.assembly_types as at on ((at.user_type_id = t.object_id) and (at.is_user_defined = 1))
join sys.assemblies as asm on asm.assembly_id = at.assembly_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @udt and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- assembly referenced by udf, sp, uda, trigger
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select asm.assembly_id, asm.name, t.object_db, @assm, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.assembly_modules as am on ((am.object_id = t.object_id) and (am.assembly_id >= 65536))
join sys.assemblies as asm on asm.assembly_id = am.assembly_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type in ( @udf, @sp, @uda, @tr) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- Partition Schemes referenced by tables/views
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select ps.data_space_id, ps.name, t.object_db, @part_sch, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.indexes as idx on idx.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.partition_schemes as ps on ps.data_space_id = idx.data_space_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type in (@u, @v) and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- Partition Function referenced by Partition Schemes
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select pf.function_id, pf.name, t.object_db, @part_func, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.partition_schemes as ps on ps.data_space_id = t.object_id
join sys.partition_functions as pf on pf.function_id = ps.function_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @part_sch and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- sp, udf, triggers referenced by plan guide
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, (case o.type when 'P' then @sp when 'TR' then @tr else @udf end), t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.plan_guides as pg on pg.plan_guide_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = pg.scope_object_id
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @pg and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- objects referenced by synonym
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select o.object_id, o.name, SCHEMA_NAME(o.schema_id), t.object_db, (case when o.type = 'U' then @u when o.type = 'V' then @v when o.type in ('P', 'RF', 'PC') then @sp when o.type = 'AF' then @uda else @udf end), t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 0, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.synonyms as s on s.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.objects as o on o.object_id = OBJECT_ID(s.base_object_name) and o.type in ('U', 'V', 'P', 'RF', 'PC', 'AF', 'TF', 'FN', 'IF', 'FS', 'FT')
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @synonym and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
-- uddt referenced by sequence. Used to find UDDT that is in sequence dependencies.
insert #t1 (object_id, object_name, object_schema, object_db, object_type, relative_id, relative_name, relative_schema, relative_db, relative_type, schema_bound, rank)
select tp.user_type_id, tp.name, SCHEMA_NAME(tp.schema_id), t.object_db, case tp.is_assembly_type when 1 then @udt else @uddt end, t.object_id, t.object_name, t.object_schema, t.object_db, t.object_type, 1, @iter_no + 1
from #t1 as t
join sys.sequences as s on s.object_id = t.object_id
join sys.types as tp on tp.user_type_id = s.user_type_id and tp.schema_id != 4
where @iter_no = t.rank and t.object_type = @sequence and (t.object_svr IS null and t.object_db = db_name())
set @rows = @rows + @@rowcount
end
set @iter_no = @iter_no + 1
end
update #t1 set rank = 0
-- computing the degree of the nodes
update #t1 set degree = (
select count(*) from #t1 t
where t.relative_id = #t1.object_id and t.object_id != t.relative_id)
-- perform the topological sorting
set @iter_no = 1
while 1 = 1
begin
update #t1 set rank=@iter_no where degree = 0
-- end the loop if no more rows left to process
if (@@rowcount = 0) break
update #t1 set degree = NULL where rank = @iter_no
update #t1 set degree = (
select count(*) from #t1 t
where t.relative_id = #t1.object_id and t.object_id != t.relative_id
and t.object_id in (select tt.object_id from #t1 tt where tt.rank = 0))
where degree is not null
set @iter_no = @iter_no + 1
end
--correcting naming mistakes of objects present in current database
--This part need to be removed once SMO's URN comparision gets fixed
DECLARE @collation sysname;
DECLARE db_cursor CURSOR
FOR
select distinct ISNULL(object_db, db_name()) from #t1 as t
where t.object_id IS NOT NULL and t.object_svr IS NULL
OPEN db_cursor
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @dbname
WHILE (@@FETCH_STATUS <> -1)
BEGIN
IF (db_id(@dbname) IS NULL)
BEGIN
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @dbname
CONTINUE
END
SET @collation = (select convert(sysname,DatabasePropertyEx(@dbname,'Collation')));
SET @query = 'update #t1 set #t1.object_name = o.name,#t1.object_schema = sch.name from #t1 inner join '+ quotename(@dbname)+ '.sys.objects as o on #t1.object_id = o.object_id inner join '+ quotename(@dbname)+ '.sys.schemas as sch on sch.schema_id = o.schema_id where o.name = #t1.object_name collate '+ @collation +' and sch.name = #t1.object_schema collate '+ @collation
EXEC (@query)
FETCH NEXT FROM db_cursor INTO @dbname
END
CLOSE db_cursor
DEALLOCATE db_cursor
--final select
select ISNULL(t.object_id, 0) as [object_id], t.object_name, ISNULL(t.object_schema, '') as [object_schema], ISNULL(t.object_db, '') as [object_db], ISNULL(t.object_svr, '') as [object_svr], t.object_type, ISNULL(t.relative_id, 0) as [relative_id], t.relative_name, ISNULL(t.relative_schema, '') as [relative_schema], relative_db, ISNULL(t.relative_svr, '') as [relative_svr], t.relative_type, t.schema_bound, ISNULL(CASE WHEN p.type= 'U' then @u when p.type = 'V' then @v end, 0) as [ptype], ISNULL(p.name, '') as [pname], ISNULL(SCHEMA_NAME(p.schema_id), '') as [pschema]
from #t1 as t
left join sys.objects as o on (t.object_type = @tr and o.object_id = t.object_id) or (t.relative_type = @tr and o.object_id = t.relative_id)
left join sys.objects as p on p.object_id = o.parent_object_id
order by rank desc
drop table #t1
drop table #t2
drop table #tempdep
IF @must_set_nocount_off > 0
set nocount off
GO
New in-built Table-Valued Function STRING_SPLIT() in SQL Server 2016 – to split strings
Till now it was bit tricky to split a Sentence or CSV String to multiple values or rows, and we used different logic to do the same.
In my [previous post] I blogged similar logic to Split a String and Combine back by using some XML syntax.
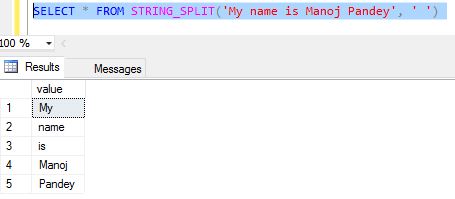
In SQL Server 2016 this has been made simpler by using a new function STRING_SPLIT(), let’s see this with a simple example:
SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT('My name is Manoj Pandey', ' ')
This will split all the words in the sentence separated by a whitespace in different rows:
Here is the syntax for the same:
STRING_SPLIT ( string , separator )
Please note: that the separator should be a single character expression, so this should not be an empty string, like:
SELECT * FROM STRING_SPLIT('My name is Manoj Pandey', '')
Will result into an error:
Msg 214, Level 16, State 11, Line 3
Procedure expects parameter ‘separator’ of type ‘nchar(1)/nvarchar(1)’.
–> Let’s check one more example:
We have a comma separated Cities list for each State as a row in a table:
CREATE TABLE #tempCityState ( [State] VARCHAR(5), [Cities] VARCHAR(50) ) INSERT INTO #tempCityState SELECT 'AK', 'Nashville,Wynne' UNION ALL SELECT 'CA', 'Fremont,Hanford,Los Anggeles' UNION ALL SELECT 'CO', 'Aspen,Denver,Teluride,Vail'
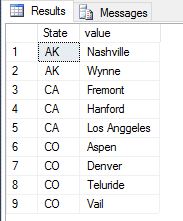
Now, lets just use the simple function STRING_SPLIT() with CROSS APPLY operator, like:
SELECT [State], value FROM #tempCityState CROSS APPLY STRING_SPLIT([Cities], ',')
Will give you following output:
–> And if I compare the performance of this function with the earlier approach I mentioned in my [previous post]:
Run both the queries by enabling Actual Execution plan (Ctrl + M):
SELECT [State], value
FROM #tempCityState
CROSS APPLY STRING_SPLIT([Cities], ',')
SELECT A.[State], Split.a.value('.', 'VARCHAR(100)') AS City
FROM (SELECT [State], CAST ('<M>' + REPLACE([Cities], ',', '</M><M>') + '</M>' AS XML) AS String
FROM #tempCityState) AS A
CROSS APPLY String.nodes ('/M') AS Split(a)
ORDER BY 1,2
I can see that the STRING_SPLIT() gives me better performance compared to the other:

Passing multiple/dynamic values to Stored Procedures & Functions | Part 5 – by passing JSON string
This post is part of the [Passing multiple/dynamic values to Stored Procedures & Functions] series, and as well as the new feature Native JSON support in SQL Server 2016.
Adding the fifth part to this series we will use JSON string that will contain the set of values and pass as an JSON param variable to the SP. Then inside the SP we will parse this JSON and use those values in our SQL Queries, just like we did in previous posts with CSV/XML strings:
USE [AdventureWorks2014]
GO
-- Create an SP with NVARCHAR type parameter for JSON string:
CREATE PROCEDURE uspGetPersonDetailsJSON (
@persons NVARCHAR(MAX)
)
AS
BEGIN
--DECLARE @persons NVARCHAR(MAX)
--SET @persons = '{"root":[{"Name":"Charles"},{"Name":"Jade"},{"Name":"Jim"},{"Name":"Luke"},{"Name":"Ken"}]}'
SELECT Name
INTO #tblPersons
FROM OPENJSON (@persons, '$.root')
WITH (
Name NVARCHAR(100)
)
SELECT
BusinessEntityID,
Title,
FirstName,
MiddleName,
LastName,
ModifiedDate
FROM [Person].[Person] PER
WHERE EXISTS (
SELECT *
FROM #tblPersons tmp
WHERE tmp.Name = PER.FirstName
)
ORDER BY FirstName, LastName
DROP TABLE #tblPersons
END
GO
-- Create JSON string:
DECLARE @json NVARCHAR(1000)
SET @json = N'{
"root": [
{ "Name": "Charles" },
{ "Name": "Jade" },
{ "Name": "Jim" },
{ "Name": "Luke" },
{ "Name": "Ken" }
]
}'
-- Use the JSON string as parameter which calling the SP:
EXEC uspGetPersonDetailsJSON @json
GO
-- Check the output, objective achieved
-- Final Cleanup
DROP PROCEDURE uspGetPersonDetailsXML
GO
Thus you can also use JSON string similar to the way you used XML string, to pass multiple and dynamic number of parameters to your Stored Procedures.
As JSON feature is new to SQL Server 2016, so this method will only work with SQL Server 2016 and above versions.
Code Review checklist for SQL Server “Stored Procedures” & T-SQL Scripts
While working on an official Database or DW/BI project we want to make sure that the Code written by team members should be correct, as per standards, with comments and beautifully indented. But everyone has a different coding style, some are good, but some are not so good, I won’t say bad :). So, to make sure everyone’s code is correct we/you introduce a process of Code Reviews.
Here in this post I’ll share some best coding practices and good to have stuff that will help others to better understand your code. The below checklist features some of them:
- Before sending any item for Code Review please make sure to do following actions:
-
– Compile the Stored Procedures, Views, T-SQL Scripts.
– For a SSRS report check the Stored Procedure by running from the Report, and check if you are getting desired output and it meets the requirement.
– If it’s an Integration SP run it for Full Load, Delta Load, and see if your are getting expected functionality.
- Before doing the check-ins ensure you do a get latest and resolve all the conflicts.
- Use TRY-CATCH to handle exceptions, and THROW clause to raise the error in CATCH clause.
- Use “;THROW” clause instead of RAISERROR() syntax. This is aligned with SQL Server future versions (> 2012) as RAISERROR is deprecated & this will reduce the code from multiple lines to just 1 line.
- Do not use TRANSACTIONs while creating Reporting or read-only Stored Procedures. Use them only in Integration SPs if the DMLs exceeds by one Query.
- Do not include #Table processing within TRANSACTIONs, and try to keep them as small as possible.
- Do not JOIN/APPLY UDFs with other tables, first extract and store records in #Tables then JOIN the #Table with other tables, otherwise it may kill performance.
- Use “WHERE EXISTS (SELECT * FROM <table>)” while evaluating Sub-Queries, and use “IN()” only while dealing with constant values.
- Use COALESCE() instead of ISNULL(), its faster & fail proof.
- Never use ISNULL() on the BIT data type, as it only accepts 1/0/NULL as the possible values.
- While comparing data against a NULLABLE column, ensure COALESCE is always used to handle records which in fact have NULLs.
- Don’t use ISNUMERIC(), use TRY_PARSE() instead.
- Do not mix DDLs & DMLs in a Stored Procedure, try to use DDLs first at the top section of SP, than use DMLs in below section. Otherwise this leads to recompilation of SP on every execution and not use the optimal cached plan.
- For temporary storage use @Table Variables for small set of records, and use #Tables for larger sets of data. Like to store Parameter values use @Table variables.
- Always use SET NOCOUNT ON statement in the beginning of SP.
- Use CTEs instead of Sub-Queries for better code manageability and readability.
- Handle Divide-by-zero errors the columns/variables occurring in denominator.
- With WHERE clause put OR conditions within brackets, otherwise they will conflict with other AND conditions and may behave differently.
- In WHERE clause use columns from a LEFT JOIN table very carefully as it may lead to convert the LEFT JOIN to an INNER JOIN or behave differently.
- Do not include DROP & CREATE statements in the CREATE table script; they should be added only In the deployment scripts.
- While designing new tables, ensure most of the columns are created as NOT NULLs.
- Please do not use “SELECT *” while creating Views, in SPs, instead get only required columns. Even if all Columns are required, list out all the columns instead of “SELECT *”.
- Do not use USE <db_name> and GO keywords in DB Object (SPs, Views, Table, etc) scripts, should be only used with Custom Pre/Post SQL Scripts.
- While CREATING or ALTERING any DB object try checking its existence by using IF-ELSE condition like:
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE TABLE_NAME = ‘TABLE_NAME’ AND TABLE_SCHEMA = ‘SCHEMA_NAME’)
BEGIN
CREATE TABLE dbo.TABLE_NAME (…)
END
- While sending Code Reviews for SSRS RDLs, also mention the URL where the reports are deployed and the changes done, with steps to populate the required params with expected O/P.
I would also like to hear from you what all things you make sure for Code Review process.
SQL Tips – Check count of records in Temporary Tables from other sessions
Recently one Stored Procedure was giving issues on our Production system. The SP had some temporary (#) tables that were getting populated in sequence, but the final result was not as expected. As Temp-Tables cannot be accessed across other sessions you cannot see what’s going on. Also as its a PROD system I could not dissect or change the SP and see what’s happening inside.
Debugging a SP on a DEV machine is simple. I can add some extra checks after temp-table population code to get the record count by using “SELECT @@rowcount”, and was able to see the issues.
But this cannot be done on PROD, as you cannot alter the SPs there. So, to see which temp table is being populated you can use below query. This will also show the records count if any temp table is in mid of population.
SELECT T.NAME AS TABLE_NAME, S.ROW_COUNT FROM TEMPDB.sys.dm_db_partition_stats AS S INNER JOIN TEMPDB.sys.tables AS T ON S.OBJECT_ID = T.OBJECT_ID WHERE S.INDEX_ID < 2 and T.NAME like '%#TempTable%'; -- Give #Table name here