Archive
SQL DBA – Disable/Enable multiple SQL Jobs at once
Seems to be a simple topic. But yes when it comes to do these type of tasks we tend to recall the syntax and end up searching internet (bing/google) for the solution.
–> Disabling a single SQL Job can be done simply through SSMS. Right click on the SQL Job and select Disable. To enable it back simply select Enable for a disabled Job.
This can also be done by a TSQL query as shown below:
USE msdb;
GO
-- Disable a SQL Job:
EXEC dbo.sp_update_job
@job_name = N'syspolicy_purge_history',
@enabled = 0 ;
GO
select enabled, * from sysjobs where name = 'syspolicy_purge_history'
GO
–> Now if you’ve to Disable Multiple or All the Jobs in SQL Agent, how will you do it?
Selecting All SQL Jobs on SSMS and right clicking won’t give you the Disable option. And here it become more tricky as there is only way to do this by TSQL query. But there is no single TSQL query defined in SQL Server to Disable all SQL Jobs at once. So, we will have to create a Dynamic SQL which will create Script for all SQL Jobs dynamically to Disable each and every SQL Job. Let’s see how:
USE msdb; GO -- Disable Multiple SQL Jobs at once: DECLARE @dynSql NVARCHAR(MAX) = '' SELECT @dynSql += N'exec msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_name = ''' + name + N''', @enabled = 0;' + CHAR(10) + CHAR(13) FROM msdb.dbo.sysjobs WHERE enabled = 1 ORDER BY name; PRINT @dynSql;
-- Here is the output of above PRINT statement: exec msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_name = 'ExecuteSPuspGetBillOfMaterials', @enabled = 0; exec msdb.dbo.sp_update_job @job_name = 'syspolicy_purge_history', @enabled = 0;
Simple Copy-Paste the the above Dynamically generated SQL Script and Execute it, it will Disable all SQL Jobs at once.
SQL Server 2012 does not support Linked Server to SQL Server 2000, workaround
Yes, you read it right, “SQL Server 2012” has stopped connecting to “SQL Server 2000” via linked Servers. As this new version uses a new Native Client version i.e. SQLNCLI11, instead of the old SQLNCLI10. This new client only connects back to 2008R2, 2008 and 2005 only.
– I upgraded my Database Servers from “SQL Server 2008 R2” to “SQL Server 2012”.
– Restored the databases from the backup taken from 2008R2.
– Ran the jobs and found that one of them was failing with following error:
Error Message:
OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “NorthWind2000” returned message “Client unable to establish connection”.
Msg 22, Level 16, State 1, Line 0
SQL Server Native Client 11.0 does not support connections to SQL Server 2000 or earlier versions.
OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “NorthWind2000” returned message “Invalid connection string attribute”.
As I have upgraded from 2008 R2, so I checked Providers under the Linked Server and found that with the new SQLNCLI11, I still have the “SQL Server Native Client 10.0” i.e. “SQLNCLI10”.
So, I tried to create the Linked Server by using “SQLNCLI10”, but it again gave an error, as follows:
Msg 8522, Level 16, State 3, Line 1
Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS DTC) has stopped this transaction.
I scripted out the DDL of my existing Linked Server, as below:
USE [master] GO -- Existing LinkedServer [NorthWind2000]: EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NorthWind2000', @srvproduct=N'MSSQL', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @provstr=N'PROVIDER=SQLOLEDB;SERVER=NorthWind' EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NorthWind2000', @useself=N'True', @locallogin=NULL, @rmtuser=NULL, @rmtpassword=NULL GO
=> WORKAROUND / FIX:
Now as a workaround to make this Linked Server work we have an option to use the ODBC Data Source which will connect to our remote server.
There are 2 approaches:
1. Either we create an ODBC Data Source (DSN) and use it in our Linked Server.
2. Or, use the Data Source (DSN) connection string directly in the Linker Server Provider.
–> Using appraoch #1:
Create an ODBC Data Source:
1. Open Control Panel, go to Administrative Tools, then “Data Sources (ODBC)”.
2. On “ODBC Data Source Administrator” window go to “System DSN” Tab.
3. Here click on Add to create a new DSN.
4. Choose “SQL Server” and click Finish.
5. On the new window, give a proper name for the Source DSN (like: NorthWind2000DSN), we will use this name while creating our Linked Server. Provide the Server name which is on SQL Server 2000, here “NorthWind”. Click Next.
6. Choose the Authentication Type, either Windows or SQL Server auth. Click Next.
7. Change the default database, not necessary. Click Next.
8. Click Finish. You will see a new DSN created under System DSN tab.
Now, create Linked Server and provide this DSN in the @datasrc param and provide the @provider param “MSDASQL”.
You can use the below query to create the same:
USE master GO -- Drop Existing LinkedServer [NorthWind2000]: EXEC sp_dropserver @server=N'NorthWind2000', @droplogins='droplogins' GO -- Re-create LinkedServer [NorthWind2000] by using the ODBC connection: EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NorthWind2000', @srvproduct=N'MSDASQL', @provider=N'MSDASQL', @datasrc = N'NorthWind2000DSN', @location=N'System'; EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NorthWind2000', @useself=N'True', @locallogin=NULL, @rmtuser=NULL, @rmtpassword=NULL GO
–> Using appraoch #2:
We can also directly put the DSN connection String in the Provider String @provstr param.
Let’s check it below:
USE master
GO
-- Drop Existing LinkedServer [NorthWind2000]:
EXEC sp_dropserver @server=N'NorthWind2000', @droplogins='droplogins'
GO
-- Re-create LinkedServer [NorthWind2000] by using the ODBC connection:
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NorthWind2000',
@srvproduct=N'',
@provider=N'MSDASQL',
@provstr=N'DRIVER={SQL Server};SERVER=NorthWind;Trusted_Connection=yes;'
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NorthWind2000',
@useself=N'True',
@locallogin=NULL,
@rmtuser=NULL,
@rmtpassword=NULL
GO
This way you can query SQL Server 2000 data from SQL Server 2012 via Linked Servers by using ODBC DSN.
This seems seamless but it is an indirect process and a workaround to query SQL Server 2000 database.
To make your queries or ETLs efficient it is advisable to upgrade to a higher version, at-least SQL Server 2005.
>> Check & Subscribe my [YouTube videos] on SQL Server.
SQL DBA – Moved MASTER database by ALTER DATABASE statement? here’s the solution
Have you also moved your MASTER DATABASE by using “ALTER DATABASE” statement just like you did for other system databases like MSDB, MODEL, TEMPDB & other databases?
If YES, then you are same nerdy DBA like me.
For quite some time I was observing very bad performance in one of our DEV servers. So today I thought to check it, I found that the C: Drive is almost full. Don’t know why do the DBA guys installed SQL Server on C: drive and put all system databases here to make it even worse. To get some room on C: drive I thought to move all four system databases (i.e. MASTER, MODEL, MSDB & TEMPDB) to another drive.
So, I created normal “ALTER DATABASE” scripts for all the 4 databases and executed them, as follows:
ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'tempdev' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\tempdb.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'templog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\templog.ldf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'modeldev' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\modeldev.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'modellog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\modellog.ldf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'MSDBData' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\MSDBData.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'MSDBLog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\MSDBLog.ldf' ) -- !!!! BEWARE DON'T RUN THIS !!!! ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'master' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\master.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'mastlog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\mastlog.ldf' ) -- !!!! BEWARE DON'T RUN THIS !!!!
-> Happily I Stopped the SQL Server service.
-> Now, to move the databases physically I moved the MDF & LDF files to the new location I used in “ALTER DATABASE” statements above.
-> After moving DB files I tried to Start the “SQL Server” service, but the service didn’t start and I was getting following error:
“The SQL Server service on [SERVER_NAME] started and then stopped. blah blah blah…”
I immediately thought that I’ve done something wrong, checked MS BOL, and found that I should not have moved the MASTER database by using “ALTER DATABASE” statement.
–> WORKAROUND:
Now when the wrong scripts are executed and there is no way to undo it, there should be some way to fix it.
SQL Server comes with a tool i.e. “SQL Server Configuration Manager” to manage the services associated with SQL Server. Like, for this case to configure startup options that will be used every time the Database Engine starts in SQL Server.
Open this tool from “Program Files -> SQL Server -> Configuration Tools”:
-> Select “SQL Server Services” on the left side navigation bar.
-> On the right side Right Click on SQL Server instance and select Properties.
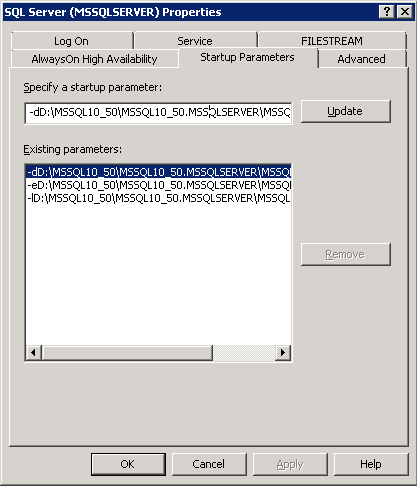
-> On the Pop-Up select the “Startup Paramaters” tab. Here you can change the MASTER database’s MDF & LDF file’s location:
—> Parameter starting with “-dD” is for DATA file (MDF).
—> AND parameter starting with “-lD” is for LOG file (LDF).
-> Select both properties one by one and change the file location at the “Existing Parameters:” text box and click Update for both the files.
-> Now, Start the Services and yes it started without any issue.
-> Check the new location by issuing either of following 2 SQL queries:
select * from sys.sysdatabases -- OR -- select * from sys.master_files
Not only this is a workaround to fix this issue, but you can also use this tool to move your MASTER database to a different Drive.
SQL Tips – Different ways to get SQL Server Version
Today I got an email form a newbee regarding some help in SQL Server.
His question was a typical “SQL Server Interview Question”: What are the various ways to get SQL Server version number?
So I researched a bit and come up with following different methods for the same, as follows:
–> Method #1:
select @@version
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (SP2) - 10.50.4000.0 (X64) Jun 28 2012 08:36:30 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation Data Center Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1) (Hypervisor)
–> Method #2:
SELECT
SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion') as ProductVersion,
SERVERPROPERTY ('productlevel') as ProductLevel,
SERVERPROPERTY ('edition') as Edition
ProductVersion ProductLevel Edition 10.50.4000.0 SP2 Data Center Edition (64-bit)
–> Method #3:
select CAST(@@microsoftversion as binary(10)) as VerBinary, @@microsoftversion / 0x01000000 as VersionNumber1, @@microsoftversion / power(2, 24) as VersionNumber2, @@microsoftversion & 0xFFFF as ReleaseNumber
VerBinary VersionNumber1 VersionNumber2 ReleaseNumber 0x0000000000000A320FA0 10 10 4000
–> Method #4:
EXEC xp_msver 'ProductVersion'
Index Name Internal_Value Character_Value 2 ProductVersion 655410 10.50.4000.0
–> Method #5:
EXEC sp_server_info
attribute_id attribute_name attribute_value 1 DBMS_NAME Microsoft SQL Server 2 DBMS_VER Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 - 10.50.4000.0 500 SYS_SPROC_VERSION 10.50.4000
–> Method #6:
Check the INSTANCE name in SSMS Object explorer. It shown SQL Server Version Number in brackets, like: (SQL Server 10.50.4000 – DOMAIN\user).
–> Method #7:
Check by “SQL Server Features Discovery report”.
Go to Start Menu -> Pragram Files -> Microsoft SQL Server -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Installation Center (64-bit)
A window will open, click on Toolsat the left navigation bar, then click on “Installed SQL Server Features Discovery report” link.
This will open up a HTML page in web-browser, which looks like in the image below:

–> Method #8:
Simply, in SSMS go to menu, Help -> About.
You will get a pop-up window which shows version number of difefrent Components installed as a part of SQL Server installation.
Passing multiple/dynamic values to Stored Procedures & Functions | Part 4 – by using TVP
This is the last fourth part of this series, in previous posts we talked about passing multiple values by following approaches: CSV, XML, #table. Here we will use a new feature introduced in SQL Server 2008, i.e. TVP (Table Valued Parameters).
As per MS BOL, TVPs are declared by using user-defined table types. We can use TVPs to send multiple rows of data to Stored Procedure or Functions, without creating a temporary table or many parameters. TVPs are passed by reference to the routines thus avoiding copy of the input data.
Let’s check how we can make use of this new feature (TVP):
-- First create a User-Defined Table type with a column that will store multiple values as multiple records:
CREATE TYPE dbo.tvpNamesList AS TABLE
(
Name NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (Name)
)
GO
-- Create the SP and use the User-Defined Table type created above and declare it as a parameter:
CREATE PROCEDURE uspGetPersonDetailsTVP (
@tvpNames tvpNamesList READONLY
)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, ModifiedDate
FROM [Person].[Person] PER
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT Name FROM @tvpNames tmp WHERE tmp.Name = PER.FirstName)
ORDER BY FirstName, LastName
END
GO
-- Now, create a Table Variable of type created above:
DECLARE @tblPersons AS tvpNamesList
INSERT INTO @tblPersons
SELECT Names FROM (VALUES ('Charles'), ('Jade'), ('Jim'), ('Luke'), ('Ken') ) AS T(Names)
-- Pass this table variable as parameter to the SP:
EXEC uspGetPersonDetailsTVP @tblPersons
GO
-- Check the output, objective achieved 🙂
-- Final Cleanup
DROP PROCEDURE uspGetPersonDetailsTVP
GO
So, we saw how we can use TVPs with Stored Procedures, similar to this they are used with UDFs.
TVPs are a great way to pass array of values as a single parameter to SPs and UDFs. There is lot of know and understand about TVP, their benefits and usage, check this [link].




