SQLNCLI11 for linked server “XYZ” returned message “Requested conversion is not supported” | SQL Server 2012 upgrade behavior changes
This was a year long pending post that got lost in my blog posts archives. Today while filtering the Posts on my Dashboard I saw this in Edit mode. So I thought to make it live after doing some edits. So, here it goes 🙂
While upgrading to SQL Server 2012 from SQL Server 2008 R2 on my DEV box, I observed some behavioral changes with SQL 2012, one ETL job that was working fine on SQL 2008 R2 was not running and throwing following error in SQL 2012:
OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “MyLocal” returned message “Requested conversion is not supported.”.
Msg 7341, Level 16, State 2, Line 1
Cannot get the current row value of column “(user generated expression).Expr1003” from OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “MyLocal”.
The above error depicts that there is something wrong with the Linked Server. But the same Linked Server was working for other tables, and it was failing for a specific table only. I checked the table and the ETL script where the Linked Server was being used. That script had a SELECT list fetching records from source table via Linked Server. The column list was having a computed column in the end like: CAST(NULL as UNIQUEIDENTIFIER) AS U_ID. I was not sure why anybody would write that code and what was the need to add this computed column. I removed this column and the error was gone. So it was clear that the CASTing of NULL to UNIQUEIDENTIFIER datatype was throwing this error, but the same code was working fine in SQL Server 2008 R2.
(Please check at the bottom of the post for more such behavioral changes)
–> Here is the issue that I’ve reproduced:
This will run fine in previous versions of SQL Server, but will throw error in 2012:
–> CREATE Linked Server
USE [master] GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'MyLocal', @srvproduct=N'MSSQL', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @datasrc=N'MANOJPANDEY-PC', -- plz change the server name here. @provstr=N'PROVIDER=SQLOLEDB;SERVER=MY-PC' -- plz change the server name here. EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'MyLocal',@useself=N'True', @locallogin=NULL,@rmtuser=NULL,@rmtpassword=NULL GO
–> Create a new table:
USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate INTO dbo.Person FROM [AdventureWorks2012].[Person].[Person]
–> Query table via Linked Server:
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate FROM [MyLocal].[AdventureWorks2012].dbo.[Person]
–> Query it after adding a column via Linked Server:
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate ,CAST(NULL as UNIQUEIDENTIFIER) AS U_ID FROM [MyLocal].[AdventureWorks2012].[dbo].[Person]
OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "MyLocal" returned message "Requested conversion is not supported.". Msg 7341, Level 16, State 2, Line 1 Cannot get the current row value of column "(user generated expression).Expr1003" from OLE DB provider "SQLNCLI11" for linked server "MyLocal".
–> Creating a View in Remote Server:
CREATE VIEW [dbo].[vwPerson] AS SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate ,CAST(NULL as UNIQUEIDENTIFIER) AS U_ID FROM [MyLocal].[AdventureWorks2012].[dbo].[Person]
–> View also fails, as it is also expanded (same error as above):
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate, U_ID FROM [MyLocal].[AdventureWorks2012].[dbo].[vwPerson]
–> Workaround 1:
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate ,CAST(CAST(0 AS BINARY) AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER) AS U_ID FROM [MyLocal].[AdventureWorks2012].[dbo].[Person]
–> Workaround 2:
SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName, Suffix, EmailPromotion, ModifiedDate ,CAST(0x AS UNIQUEIDENTIFIER) AS U_ID FROM [MyLocal].[AdventureWorks2012].[dbo].[Person]
–> Final Cleanup:
DROP TABLE dbo.Person DROP VIEW dbo.vwPerson GO USE [master] GO EXEC master.dbo.sp_dropserver @server=N'MyLocal', @droplogins='droplogins' GO
–> I’ve documented more behavioral changes after SQL Server 2012 upgrade, and here is the list:
2. Temp #Tables created with negative IDs
3. No native Linked Server support to SQL Server 2000
GROUPING SETS equivalent | for SQL Server 2005 and below
Sometime back I discussed about [GROUPING SETS] in my previous post and today one reader of this blog asked me how we can create the same result-set without using GROUPING SETS if we are on previous versions like SQL Server 2005 or 2000.
–> Let’s take the following SQL Query that uses GROUPING SETS operator and let’s see what Output we get:
-- GROUPING SETS SELECT class, section, rollno, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ( (class, section, rollno) ,(class, section) ,(class) ,() )
Output:
class section rollno sum
HighSchool a 1 80
HighSchool a 2 70
HighSchool a 3 80
HighSchool a NULL 230
HighSchool b 4 90
HighSchool b 5 90
HighSchool b 6 50
HighSchool b NULL 230
HighSchool NULL NULL 460
Intermediate a 1 60
Intermediate a 2 50
Intermediate a 3 80
Intermediate a NULL 190
Intermediate b 4 90
Intermediate b 5 50
Intermediate b 6 70
Intermediate b NULL 210
Intermediate NULL NULL 400
NULL NULL NULL 860
You can refer to the DDL and population of this #tempTable in my previous post, [link].
–> And now let’s see how can we recreate the same result set without using GROUPING SETS if we are on lower versions of SQL Server (<= 2005):
-- ROLLUP and Grouping Sets Equivalent (pre SQL 2008) SELECT class, section, rollno, marks as [sum] FROM #tempTable UNION ALL SELECT class, section, null as rollnu, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable GROUP BY class, section UNION ALL SELECT class, null, null, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable GROUP BY class UNION ALL SELECT null, null, null, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable ORDER BY class DESC, section DESC, rollno DESC
Thanks, please let me know your thoughts and comments!!!
Dynamic SQL usage, when to use? – MSDN TSQL forum
–> Question:
Can someone tell when or where to use Dynamic SQL ( exec sp_executesql and exec commands) over normal SQL?
–> My Answer:
Dynamic SQL queries should be avoided and one should put more thought and time on creating non-dynamic SQL statements.
But there could be some rare scenarios or requirements where you need to create Dynamic SQL, like doing some multiple DBA activities in one go, like:
– Enabling/Disabling multiple Jobs at once, link.
– Creating Dynamic PIVOT where there could be multiple columns based on multiple rows, link.
– Use sp_executeSQL instead of EXEC (SQL statement) to avoid SQL-Injection.
– Check this article by Erland on Dynamic SQL.
– Check this blog post for EXEC (SQL statement) vs sp_executeSQL.
Ref Link.
SQL Basics – What are Row Constructors?
Constructors, as the name suggests means to create an instance of an Object in any Object Oriented Programming language.
Here in SQL Server or T-SQL, ROW Constructor or Table Value Constructor means to create a row set by using the VALUES() clause. This allows multiple rows of data to be specified in a single DML statement. And this VALUES() clause can be used with the SELECT, INSERT and MERGE statements.
In the examples below we will see how they can be used and are helpful at times:
Usage #1. You can create a simple set of rows with a SELECT FROM statement:
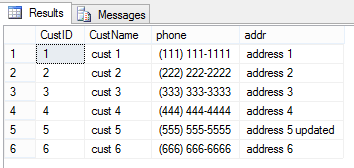
SELECT * FROM ( VALUES (1, 'cust 1', '(111) 111-1111', 'address 1'), (2, 'cust 2', '(222) 222-2222', 'address 2'), (3, 'cust 3', '(333) 333-3333', 'address 3'), (4, 'cust 4', '(444) 444-4444', 'address 4'), (5, 'cust 5', '(555) 555-5555', 'address 5') ) AS C (CustID, CustName, phone, addr);
Usage #2. You can use it with INSERT statement while inserting rows in a table:
CREATE TABLE dbo.Customer ( CustID INT, CustName VARCHAR(100), phone VARCHAR(20), addr VARCHAR(500) ) INSERT INTO dbo.Customer (CustID, CustName, phone, addr) VALUES (1, 'cust 1', '(111) 111-1111', 'address 1'), (2, 'cust 2', '(222) 222-2222', 'address 2'), (3, 'cust 3', '(333) 333-3333', 'address 3'), (4, 'cust 4', '(444) 444-4444', 'address 4'), (5, 'cust 5', '(555) 555-5555', 'address 5');
Usage #3. You can create mixed row-sets from manually entered values and from other tables:
SELECT * FROM ( VALUES (1, 'cust 1', '(111) 111-1111', 'address 1'), (2, 'cust 2', '(222) 222-2222', 'address 2'), (3, 'cust 3', '(333) 333-3333', 'address 3'), (4, 'cust 4', '(444) 444-4444', 'address 4'), ((SELECT CustID FROM dbo.Customer WHERE CustID IN (5)), (SELECT CustName FROM dbo.Customer WHERE CustID IN (5)), (SELECT phone FROM dbo.Customer WHERE CustID IN (5)), (SELECT addr FROM dbo.Customer WHERE CustID IN (5)) ) ) AS C (CustID, CustName, phone, addr);
Usage #4. You can use them with JOINS, without need to create #Temp-Table or Table-Variable to store temporary data:
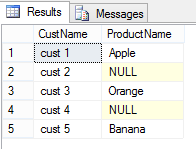
SELECT C.CustName, O.ProductName FROM dbo.Customer C LEFT JOIN ( VALUES (101, 1, 'Apple'), (102, 3, 'Orange'), (103, 5, 'Banana') ) AS O (OrderID ,CustID, ProductName) ON O.CustID = C.CustID
Usage #5. You can use them with MERGE statement, again without need to create #Temp-Table or Table-Variable to store temporary data:
MERGE INTO dbo.Customer as Target USING ( VALUES (5, 'cust 5', '(555) 555-5555', 'address 5 updated'), (6, 'cust 6', '(666) 666-6666', 'address 6') ) AS Source (CustID, CustName, phone, addr) ON Target.CustID = Source.CustID WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET Target.CustName = Source.CustName, Target.phone = Source.phone, Target.addr = Source.addr WHEN NOT MATCHED BY Target THEN INSERT ( CustID, CustName, phone, addr ) VALUES ( Source.CustID, Source.CustName, Source.phone, Source.addr ); select * from dbo.Customer;
Thus, Row Constructors or Table Value Constructors are very handy when dealing with fixed set of row sets used for temporary purpose, without need of creating and storing them in #Temp-Tables or Table-Variables.
–> Final Cleanup
DROP TABLE dbo.Customer
Capture multiple errors in TRY CATCH by using THROW statement
This post relates to my earlier post [link] where I mentioned on benefit of using THROW clause with same SQL examples.
The THROW clause was introduced in SQL Server 2012 and may be replacing the RAISERROR function in near future.
Normally the SQL statements returns single error, but some SQL statements returns more than one error message when they go wrong due to some reason or exception.
–> On executing the below BACKUP statement in SSMS we can see we get two errors:
BACKUP DATABASE [AdventureWorks2012] TO DISK='E:\FOLDER_NOT_EXISTS\test.bak'
The above code throws 2 errors with Error-Message IDs 3201 & 3013, as shown below:
error messages:
Msg 3201, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Cannot open backup device ‘E:\FOLDER_NOT_EXISTS\test.bak’. Operating system error 3(The system cannot find the path specified.).
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
-> But when we want to track these errors by using RAISERROR function it just returns the last (single) error message and its details, and the previous error message details are not returned by this function.
BEGIN TRY BACKUP DATABASE [AdventureWorks2012] TO DISK='E:\FOLDER_NOT_EXISTS\test.bak' END TRY BEGIN CATCH DECLARE @msg VARCHAR(1000) = ERROR_MESSAGE() RAISERROR(@msg,16,0) END CATCH
Here, only 1 error message will be returned:
error messages:
Msg 50000, Level 16, State 0, Line 7
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
–> With the new THROW clause you won’t see any issue of omitting the previous errors, as it returns all error details thrown by the SQL Statement itself.
BEGIN TRY BACKUP DATABASE [AdventureWorks2012] TO DISK='E:\FOLDER_NOT_EXISTS\test.bak' END TRY BEGIN CATCH THROW; END CATCH
The above statement throws both the error details as we saw in the first example:
error messages:
Msg 3201, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Cannot open backup device ‘E:\FOLDER_NOT_EXISTS\test.bak’. Operating system error 3(The system cannot find the path specified.).
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
BACKUP DATABASE is terminating abnormally.
Thus, if you are on SQL Server 2012 and above you must consider using THROW clause instead of the RAISERROR function.