SQL Server vNext (2012) coming up with lot a new features | Hekaton, Polybase, PDW, and many more
This year’s PASS Summit Microsoft announced lot of new features coming up for “SQL Server 2012” and version vNext.
1. Released SQL Server 2012 Service Pack 1: with bug fixes and lot of improvements, like Selective XML Indexes & enhancements in Self-Service BI & Excel 2013.

2. Column Store Indexes: will be extended to be created with Clustered Indexes as well.
3. Hekaton & Polybase: will be major ingredients in SQL Server vNext by 2014-15.
4. SQL Server version Next: will use Hekaton for its OLTP database to take database objects into in-memory and “memory optimize” tables, thus challenging SAP-Hana and Oracle much hyped Exadata soluition.
5. SQL Server 2012 PDW: (Parallel Data Warehouse) will be using Polybase to interact between PDW and Hadoop clusters.
… I’ll be discussing more about these things in next posts, so keep tuned!!!
SQL Server 2012 | Temp Tables are created with negative Object IDs
These days I’m working on SQL Server upgrade from 2008 R2 to 2012 for one of our project module.
Today while working on it I got blocked while installing a Build. The build was failing with following error:
Error SQL72014: .Net SqlClient Data Provider: Msg 2714, Level 16, State 6, Line 115 There is already an object named ‘#temp’ in the database.
I checked the code and found the line where it was failing:
IF object_id('tempdb.dbo.#temp') > 0
DROP TABLE #temp
I checked this code with SQL Server 2008 R2 and it was working perfectly.
So to check and validate this I created a temp-table on SQL Server 2012 and found that it is created by negative Object ID, check this:
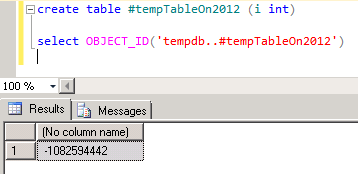
This is a new change done with SQL 2012 version, but this is not mentioned anywhere in MSDN BOL.
So, to make this legacy code work we have to re-factor all such cases, by:
IF object_id('tempdb.dbo.#temp') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #temp
Confirmation form Microsoft SQL team blog [CSS SQL Server Engineers]:
“in SQL Server 2012, we made a conscious change to the algorithm so that objectids for user-defined temporary tables would be a particular range of values. Most of the time we use hex arithmetic to define these ranges and for this new algorithm these hex values spill into a specific set of negative numbers for object_id, which is a signed integer or LONG type. So in SQL Server 2012, you will now always see object_id values < 0 for user-defined temp tables when looking at a catalog view like sys.objects.”
More Info on: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/psssql/archive/2012/09/09/revisiting-inside-tempdb.aspx
SQL DBA – Moved MASTER database by ALTER DATABASE statement? here’s the solution
Have you also moved your MASTER DATABASE by using “ALTER DATABASE” statement just like you did for other system databases like MSDB, MODEL, TEMPDB & other databases?
If YES, then you are same nerdy DBA like me.
For quite some time I was observing very bad performance in one of our DEV servers. So today I thought to check it, I found that the C: Drive is almost full. Don’t know why do the DBA guys installed SQL Server on C: drive and put all system databases here to make it even worse. To get some room on C: drive I thought to move all four system databases (i.e. MASTER, MODEL, MSDB & TEMPDB) to another drive.
So, I created normal “ALTER DATABASE” scripts for all the 4 databases and executed them, as follows:
ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'tempdev' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\tempdb.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'templog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\templog.ldf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'modeldev' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\modeldev.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'modellog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\modellog.ldf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'MSDBData' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\MSDBData.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'MSDBLog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\MSDBLog.ldf' ) -- !!!! BEWARE DON'T RUN THIS !!!! ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'master' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\master.mdf' ) ALTER DATABASE master MODIFY FILE ( NAME = 'mastlog' , FILENAME = 'D:\MSSQL10_50\MSSQL10_50.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\mastlog.ldf' ) -- !!!! BEWARE DON'T RUN THIS !!!!
-> Happily I Stopped the SQL Server service.
-> Now, to move the databases physically I moved the MDF & LDF files to the new location I used in “ALTER DATABASE” statements above.
-> After moving DB files I tried to Start the “SQL Server” service, but the service didn’t start and I was getting following error:
“The SQL Server service on [SERVER_NAME] started and then stopped. blah blah blah…”
I immediately thought that I’ve done something wrong, checked MS BOL, and found that I should not have moved the MASTER database by using “ALTER DATABASE” statement.
–> WORKAROUND:
Now when the wrong scripts are executed and there is no way to undo it, there should be some way to fix it.
SQL Server comes with a tool i.e. “SQL Server Configuration Manager” to manage the services associated with SQL Server. Like, for this case to configure startup options that will be used every time the Database Engine starts in SQL Server.
Open this tool from “Program Files -> SQL Server -> Configuration Tools”:
-> Select “SQL Server Services” on the left side navigation bar.
-> On the right side Right Click on SQL Server instance and select Properties.
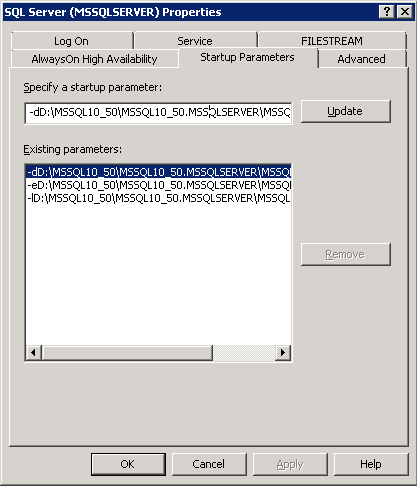
-> On the Pop-Up select the “Startup Paramaters” tab. Here you can change the MASTER database’s MDF & LDF file’s location:
—> Parameter starting with “-dD” is for DATA file (MDF).
—> AND parameter starting with “-lD” is for LOG file (LDF).
-> Select both properties one by one and change the file location at the “Existing Parameters:” text box and click Update for both the files.
-> Now, Start the Services and yes it started without any issue.
-> Check the new location by issuing either of following 2 SQL queries:
select * from sys.sysdatabases -- OR -- select * from sys.master_files
Not only this is a workaround to fix this issue, but you can also use this tool to move your MASTER database to a different Drive.
SQL Tips – Different ways to get SQL Server Version
Today I got an email form a newbee regarding some help in SQL Server.
His question was a typical “SQL Server Interview Question”: What are the various ways to get SQL Server version number?
So I researched a bit and come up with following different methods for the same, as follows:
–> Method #1:
select @@version
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 (SP2) - 10.50.4000.0 (X64) Jun 28 2012 08:36:30 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation Data Center Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1) (Hypervisor)
–> Method #2:
SELECT
SERVERPROPERTY ('productversion') as ProductVersion,
SERVERPROPERTY ('productlevel') as ProductLevel,
SERVERPROPERTY ('edition') as Edition
ProductVersion ProductLevel Edition 10.50.4000.0 SP2 Data Center Edition (64-bit)
–> Method #3:
select CAST(@@microsoftversion as binary(10)) as VerBinary, @@microsoftversion / 0x01000000 as VersionNumber1, @@microsoftversion / power(2, 24) as VersionNumber2, @@microsoftversion & 0xFFFF as ReleaseNumber
VerBinary VersionNumber1 VersionNumber2 ReleaseNumber 0x0000000000000A320FA0 10 10 4000
–> Method #4:
EXEC xp_msver 'ProductVersion'
Index Name Internal_Value Character_Value 2 ProductVersion 655410 10.50.4000.0
–> Method #5:
EXEC sp_server_info
attribute_id attribute_name attribute_value 1 DBMS_NAME Microsoft SQL Server 2 DBMS_VER Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 - 10.50.4000.0 500 SYS_SPROC_VERSION 10.50.4000
–> Method #6:
Check the INSTANCE name in SSMS Object explorer. It shown SQL Server Version Number in brackets, like: (SQL Server 10.50.4000 – DOMAIN\user).
–> Method #7:
Check by “SQL Server Features Discovery report”.
Go to Start Menu -> Pragram Files -> Microsoft SQL Server -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Installation Center (64-bit)
A window will open, click on Toolsat the left navigation bar, then click on “Installed SQL Server Features Discovery report” link.
This will open up a HTML page in web-browser, which looks like in the image below:

–> Method #8:
Simply, in SSMS go to menu, Help -> About.
You will get a pop-up window which shows version number of difefrent Components installed as a part of SQL Server installation.