Archive
C++ Graphics – 06 – Translation of LINE, TRIANGLE and RECTANGLE
Translation of LINE, TRIANGLE and RECTANGLE.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <graphics.h>
const int MAX = 5;
void GetCords(int mat[][MAX], int n){
int i, j;
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
printf("\n Enter Coordinate no %d:- \n", i+1);
for(j=0; j<2; j++){
scanf("%d", &mat[j][i]);
}
}
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
mat[0][i] = 320 + mat[0][i];
mat[1][i] = 240 - mat[1][i];
}
setcolor(GREEN);
line(0, 240, 640, 240);
outtextxy(630, 245, "x");
line(320, 0, 320, 480);
outtextxy(310, 0, "y");
outtextxy(280, 245, "(0,0)");
setcolor(YELLOW);
moveto(mat[0][0], mat[1][0]);
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
lineto(mat[0][i], mat[1][i]);
moveto(mat[0][i], mat[1][i]);
}
lineto(mat[0][0], mat[1][0]);
}
void Transform(int mat[][MAX], int n){
int dx, dy, i;
printf("\n Enter Cordinates (dx, dy):- \n");
scanf("%d %d", &dx, &dy);
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
mat[0][i] += dx;
mat[1][i] -= dy;
}
setcolor(LIGHTRED);
moveto(mat[0][0], mat[1][0]);
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
lineto(mat[0][i], mat[1][i]);
moveto(mat[0][i], mat[1][i]);
}
lineto(mat[0][0], mat[1][0]);
}
void main(){
int gd=DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm,"\\tc");
int mat[MAX][MAX], n;
int ch;
while(1){
clrscr();
cleardevice();
printf("\n TRANSFORAMTION ");
printf("\n ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n");
printf("\n 1 -> LINE.");
printf("\n 2 -> TRIANGLE.");
printf("\n 3 -> RECTANGLE");
printf("\n 4 -> Exit.");
printf("\n Enter your choice: ");
scanf("%d", &ch);
clrscr();
cleardevice();
switch(ch){
case 1: // LINE.
n=2;
break;
case 2: // TRIANGLE.
n=3;
break;
case 3: // RECTANGLE.
n=4;
break;
default:
gotoxy(10, 10);
printf(" Dev. By: Manoj Pandey.");
gotoxy(15, 15);
printf("MCA 3d Sem.");
getch();
closegraph();
exit(1);
} // end of switch.
GetCords(mat, n); // Input of Coordinates.
Transform(mat, n); // Translating and Displaying.
getch();
} // end of while.
} // end of main.
C++ Graphics – 05 – Ellipse program by Midpoint Algorithm
Ellipse Program by Midpoint Algorithm.
Similarly to the Circle Midpoint algorithm this algorithm also draws all eight octants simultaneously, starting from each cardinal direction (0°, 90°, 180°, 270°) and extends both ways to reach the nearest multiple of 45° (45°, 135°, 225°, 315°).
#include <graphics.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <dos.h>
void ellipsePoint(int x, int y){
putpixel(x+320, y+240, WHITE);
putpixel(y+320, x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(y+320, -x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(x+320, -y+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-x+320, -y+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-y+320, -x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-y+320, x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-x+320, y+240, WHITE);
}
void ellipseMidPoint(int a, int b){
double d2;
int x=0;
int y=b;
double d1 = b*b-(a*a*b)+(0.25*a*a);
ellipsePoint(x, y);
while( (a*a*(y-0.5)) > (b*b*(x+1)) ){
if(d1 < 0)
d1 += b*b*(2*x+3);
else{
d1 += b*b*(2*x+3)+a*a*(-2*y+2);
y--;
}
x++;
ellipsePoint(x, y);
}
d2 = b*b*(x+0.5)*(x+0.5)+a*a*(y-1)*(y-1)-a*a*b*b;
while(y > 0){
if(d2 < 0){
d2 += b*b*(2*x+2)+a*a*(-2*y+3);
x++;
}
else
d2 += a*a*(-2*y+3);
y--;
ellipsePoint(x, y);
}
}
void main(){
int gd=DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "e:\\tc\\");
ellipseMidPoint(100, 200);
getch();
closegraph();
}
C++ Graphics – 04 – Circle program by Midpoint Algorithm
Circle program by Midpoint Algorithm.
This algorithm draws all eight octants simultaneously, starting from each cardinal direction (0°, 90°, 180°, 270°) and extends both ways to reach the nearest multiple of 45° (45°, 135°, 225°, 315°). You can determine where to stop because when y = x, you have reached 45°.
#include <graphics.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <dos.h>
void CirclePoints(int x, int y){
putpixel(x+320, y+240, WHITE);
putpixel(y+320, x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(y+320, -x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(x+320, -y+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-x+320, -y+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-y+320, -x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-y+320, x+240, WHITE);
putpixel(-x+320, y+240, WHITE);
}
void MidPointCircle(int r){
int x = 0;
int y = r;
double d = 5.0/4.0 - r;
CirclePoints(x, y);
while(y > x){
if(d < 0)
d += 2.0 * x + 3.0;
else{
d += 2.0 * (x - y) + 5.0;
y--;
}
x++;
CirclePoints(x, y);
delay(50);
}
}
void main(){
int gd=DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "\\tc");
MidPointCircle(200);
getch();
closegraph();
}
Bresenham’s Circle algorithm is derived from the Midpoint Circle algorithm.
C++ Graphics – 03 – Line program by DDA Algorithm
Line Program by DDA or Digital differential Analyzer algorithm.
This algorithm is used for linear interpolation of variables over an interval between start and end point.
The DDA starts by calculating the smaller of dy or dx for a unit increment of the other. A line is then sampled at unit intervals in one coordinate and corresponding integer values nearest the line path are determined for the other coordinate.
Considering a line with positive slope, if the slope is less than or equal to 1, we sample at unit x intervals (dx=1) and compute successive y values as
Subscript k takes integer values starting from 0, for the 1st point and increases by 1 until endpoint is reached. y value is rounded off to nearest integer to correspond to a screen pixel.
For lines with slope greater than 1, we reverse the role of x and y i.e. we sample at dy=1 and calculate consecutive x values as
Similar calculations are carried out to determine pixel positions along a line with negative slope. Thus, if the absolute value of the slope is less than 1, we set dx=1 if 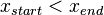 i.e. the starting extreme point is at the left.
i.e. the starting extreme point is at the left.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <math.h>
void lineDDA(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
int x, y, k;
float dy = y2-y1;
float dx = x2-x1;
int step, xinc, yinc;
if (abs(dx) > abs(dy))
step = dx;
else
step = dy;
x = x1;
y = y1;
putpixel(x, y, WHITE);
xinc = dx/step;
yinc = dy/step;
for(k=0; k<step; k++){
x += xinc;
y += yinc;
putpixel(x, y, WHITE);
}
}
void main() {
int gd=DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "\\tc");
lineDDA(300, 100, 100, 400);
getch();
}
C++ Graphics – 02 – Line program by Incremental Algorithm
Create a Line program by Incremental Algorithm.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <graphics.h>
#include <math.h>
void lineIncremental(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2){
int x;
float dy = y2-y1;
float dx = x2-x1;
float m = dy/dx;
float y = y1;
if ((m > -1) || (m < 1) ){
for(x=x1; x<=x2;x++){
putpixel(x, floor(0.5+y), WHITE);
y+=m;
}
}
else{
for(x=y1; x<=y2;x++){
putpixel(x, floor(0.5+y), WHITE);
x+=1/m;
}
}
}
void main(){
int gd=DETECT, gm;
initgraph(&gd, &gm, "\\tc");
lineIncremental(100, 10, 300, 400);
lineIncremental(100, 400, 300, 10);
getch();
}






