Archive
New THROW statement in SQL Server 2012 (vs RAISERROR)
Newly introduced THROW keyword in SQL server 2012 is an improvement over the existing RAISERROR() statement. Yes, it’s single ‘E’ in RAISERROR.
Both RAISERROR & THROW can be used in T-SQL code/script to raise and throw error within a TRY-CATCH block. Check my previous post for TRY-CATCH block, [link].
–> With RAISERROR developers had to use different ERROR_xxxx() system functions to get the error details to pass through the RAISERROR() statement, like:
– ERROR_NUMBER()
– ERROR_MESSAGE()
– ERROR_SEVERITY()
– ERROR_STATE()
let’s see an example:
-- Using RAISERROR() DECLARE @ERR_MSG AS NVARCHAR(4000) ,@ERR_SEV AS SMALLINT ,@ERR_STA AS SMALLINT BEGIN TRY SELECT 1/0 as DivideByZero END TRY BEGIN CATCH SELECT @ERR_MSG = ERROR_MESSAGE(), @ERR_SEV =ERROR_SEVERITY(), @ERR_STA = ERROR_STATE() SET @ERR_MSG= 'Error occurred while retrieving the data from database: ' + @ERR_MSG RAISERROR (@ERR_MSG, @ERR_SEV, @ERR_STA) WITH NOWAIT END CATCH GO
Output:
(0 row(s) affected)
Msg 50000, Level 16, State 1, Line 15
Error occurred while retrieving the data from database: Divide by zero error encountered.
The RAISERROR() can take first argument as message_id also instead of the message. But if you want to pass the message_id then it has to be in sys.messages
–> With THROW the benefit is: it is not mandatory to pass any parameter to raise an exception.
Just using the THROW; statement will get the error details and raise it, as shown below:
-- Using THROW - 1 BEGIN TRY SELECT 1/0 as DivideByZero END TRY BEGIN CATCH THROW; END CATCH GO
Output:
(0 row(s) affected)
Msg 8134, Level 16, State 1, Line 2
Divide by zero error encountered.
As you see in the Output above, the error message thrown is the default one. But you can also add your customized message, we will see below.
IMP NOTE: THROW will show the exact line where the exception was occurred, here the line number is 2. But RAISERROR will show the line number where the RAISERROR statement was executed i.e. Line 15, but not the actual exception position.
Also passing the message_id won’t require it to be stored in sys.messages, let’s check this:
-- Using THROW - 2 DECLARE @ERR_MSG AS NVARCHAR(4000) ,@ERR_STA AS SMALLINT BEGIN TRY SELECT 1/0 as DivideByZero END TRY BEGIN CATCH SELECT @ERR_MSG = ERROR_MESSAGE(), @ERR_STA = ERROR_STATE() SET @ERR_MSG= 'Error occurred while retrieving the data from database: ' + @ERR_MSG; THROW 50001, @ERR_MSG, @ERR_STA; END CATCH GO
Output:
(0 row(s) affected)
Msg 50001, Level 16, State 1, Line 14
Error occurred while retrieving the data from database: Divide by zero error encountered.
But if you parameterize the THROW statement as above it will not show the actual position of exception occurrence, and the behavior will be same as RAISERROR(). As with RAISERROR() you’ve to provide mandatory params, so there is no way to get the actual position of Line where the error occurred.
As per MSBOL following are the difference between RAISERROR & THROW:
|
RAISERROR statement |
THROW statement |
|---|---|
|
If a msg_id is passed to RAISERROR, the ID must be defined in sys.messages. |
The error_number parameter does not have to be defined in sys.messages. |
|
The msg_str parameter can contain printf formatting styles. |
The message parameter does not accept printf style formatting. |
|
The severity parameter specifies the severity of the exception. |
There is no severity parameter. The exception severity is always set to 16. |
NOTE: As per MS BOL for exception handling in new development work THROW must be used instead of RAISERROR.
SQL Server 2012 does not support Linked Server to SQL Server 2000, workaround
Yes, you read it right, “SQL Server 2012” has stopped connecting to “SQL Server 2000” via linked Servers. As this new version uses a new Native Client version i.e. SQLNCLI11, instead of the old SQLNCLI10. This new client only connects back to 2008R2, 2008 and 2005 only.
– I upgraded my Database Servers from “SQL Server 2008 R2” to “SQL Server 2012”.
– Restored the databases from the backup taken from 2008R2.
– Ran the jobs and found that one of them was failing with following error:
Error Message:
OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “NorthWind2000” returned message “Client unable to establish connection”.
Msg 22, Level 16, State 1, Line 0
SQL Server Native Client 11.0 does not support connections to SQL Server 2000 or earlier versions.
OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “NorthWind2000” returned message “Invalid connection string attribute”.
As I have upgraded from 2008 R2, so I checked Providers under the Linked Server and found that with the new SQLNCLI11, I still have the “SQL Server Native Client 10.0” i.e. “SQLNCLI10”.
So, I tried to create the Linked Server by using “SQLNCLI10”, but it again gave an error, as follows:
Msg 8522, Level 16, State 3, Line 1
Microsoft Distributed Transaction Coordinator (MS DTC) has stopped this transaction.
I scripted out the DDL of my existing Linked Server, as below:
USE [master] GO -- Existing LinkedServer [NorthWind2000]: EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NorthWind2000', @srvproduct=N'MSSQL', @provider=N'SQLNCLI', @provstr=N'PROVIDER=SQLOLEDB;SERVER=NorthWind' EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NorthWind2000', @useself=N'True', @locallogin=NULL, @rmtuser=NULL, @rmtpassword=NULL GO
=> WORKAROUND / FIX:
Now as a workaround to make this Linked Server work we have an option to use the ODBC Data Source which will connect to our remote server.
There are 2 approaches:
1. Either we create an ODBC Data Source (DSN) and use it in our Linked Server.
2. Or, use the Data Source (DSN) connection string directly in the Linker Server Provider.
–> Using appraoch #1:
Create an ODBC Data Source:
1. Open Control Panel, go to Administrative Tools, then “Data Sources (ODBC)”.
2. On “ODBC Data Source Administrator” window go to “System DSN” Tab.
3. Here click on Add to create a new DSN.
4. Choose “SQL Server” and click Finish.
5. On the new window, give a proper name for the Source DSN (like: NorthWind2000DSN), we will use this name while creating our Linked Server. Provide the Server name which is on SQL Server 2000, here “NorthWind”. Click Next.
6. Choose the Authentication Type, either Windows or SQL Server auth. Click Next.
7. Change the default database, not necessary. Click Next.
8. Click Finish. You will see a new DSN created under System DSN tab.
Now, create Linked Server and provide this DSN in the @datasrc param and provide the @provider param “MSDASQL”.
You can use the below query to create the same:
USE master GO -- Drop Existing LinkedServer [NorthWind2000]: EXEC sp_dropserver @server=N'NorthWind2000', @droplogins='droplogins' GO -- Re-create LinkedServer [NorthWind2000] by using the ODBC connection: EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NorthWind2000', @srvproduct=N'MSDASQL', @provider=N'MSDASQL', @datasrc = N'NorthWind2000DSN', @location=N'System'; EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NorthWind2000', @useself=N'True', @locallogin=NULL, @rmtuser=NULL, @rmtpassword=NULL GO
–> Using appraoch #2:
We can also directly put the DSN connection String in the Provider String @provstr param.
Let’s check it below:
USE master
GO
-- Drop Existing LinkedServer [NorthWind2000]:
EXEC sp_dropserver @server=N'NorthWind2000', @droplogins='droplogins'
GO
-- Re-create LinkedServer [NorthWind2000] by using the ODBC connection:
EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'NorthWind2000',
@srvproduct=N'',
@provider=N'MSDASQL',
@provstr=N'DRIVER={SQL Server};SERVER=NorthWind;Trusted_Connection=yes;'
EXEC sp_addlinkedsrvlogin @rmtsrvname=N'NorthWind2000',
@useself=N'True',
@locallogin=NULL,
@rmtuser=NULL,
@rmtpassword=NULL
GO
This way you can query SQL Server 2000 data from SQL Server 2012 via Linked Servers by using ODBC DSN.
This seems seamless but it is an indirect process and a workaround to query SQL Server 2000 database.
To make your queries or ETLs efficient it is advisable to upgrade to a higher version, at-least SQL Server 2005.
>> Check & Subscribe my [YouTube videos] on SQL Server.
SQL Server 2012 | Temp Tables are created with negative Object IDs
These days I’m working on SQL Server upgrade from 2008 R2 to 2012 for one of our project module.
Today while working on it I got blocked while installing a Build. The build was failing with following error:
Error SQL72014: .Net SqlClient Data Provider: Msg 2714, Level 16, State 6, Line 115 There is already an object named ‘#temp’ in the database.
I checked the code and found the line where it was failing:
IF object_id('tempdb.dbo.#temp') > 0
DROP TABLE #temp
I checked this code with SQL Server 2008 R2 and it was working perfectly.
So to check and validate this I created a temp-table on SQL Server 2012 and found that it is created by negative Object ID, check this:
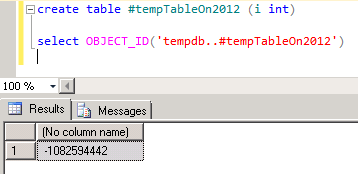
This is a new change done with SQL 2012 version, but this is not mentioned anywhere in MSDN BOL.
So, to make this legacy code work we have to re-factor all such cases, by:
IF object_id('tempdb.dbo.#temp') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #temp
Confirmation form Microsoft SQL team blog [CSS SQL Server Engineers]:
“in SQL Server 2012, we made a conscious change to the algorithm so that objectids for user-defined temporary tables would be a particular range of values. Most of the time we use hex arithmetic to define these ranges and for this new algorithm these hex values spill into a specific set of negative numbers for object_id, which is a signed integer or LONG type. So in SQL Server 2012, you will now always see object_id values < 0 for user-defined temp tables when looking at a catalog view like sys.objects.”
More Info on: http://blogs.msdn.com/b/psssql/archive/2012/09/09/revisiting-inside-tempdb.aspx
SQL DBA – Upgrade to SQL Server 2012 – Use Upgrade Advisor
Are you planning to upgrade your SQL Servers to 2012? YES!
How will you make sure that you are ready for Upgrade? ???
How will you make sure that the Upgrade will be seamless? 😦
SQL Server 2012 “Upgrade Advisor” is for you to check and analyze instances of all previous SQL Server versions i.e. 2008 R2, 2008, 2005 and even 2000 in preparation for upgrading to SQL Server 2012.
“Upgrade Advisor” identifies all features and configuration changes that might affect your upgrade. It provides links to documentation that describes each identified issue and how to resolve it and also generates a report that captures identified issues to fix either before or after you upgrade.
This tool has some prerequisites to install, and if you don’t install them you might see following error while installation:
Setup is missing prerequisites: -Microsoft SQL Server 2012 Transact-SQL Script DOM, which is not installed by Upgrade Advisor Setup. To continue, install SQL Server 2012 Transact-SQL Script DOM from below hyperlink and then run the Upgrade Advisor Setup operation again : Go to http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=216742
The above error mentions to install “MS SQL Server 2012 Transact-SQL ScriptDom” component. Install it from here: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=29065&ocid=aff-n-we-loc–ITPRO40886&WT.mc_id=aff-n-we-loc–ITPRO40886
But for this also “MS DOT NET 4.0” is required on your system. To Install it check this link: http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=17851
After installing Upgrade Advisor, launch the tool, it gives you 2 options:
1. Launch Upgrade Advisor Analysis Wizard
2. Report Upgrade Advisor Viewer
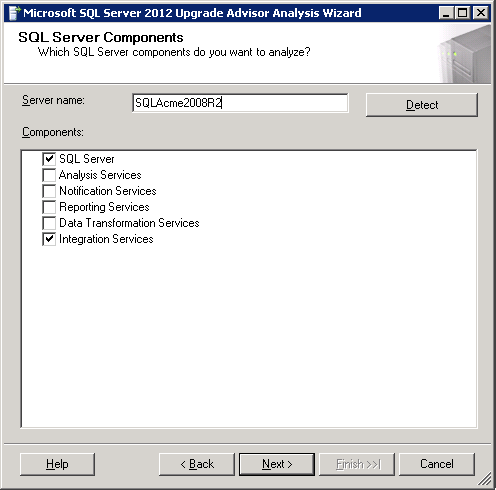
–> Analysis Wizard lets you run alanysis on following SQL components shown in image below:
–> Report Viewer tell you about the changes that needs attention or needs change/fix before or after upgrading to 2012. After Analysis Wizard finishes it creates repots which is in the form of an XML file.
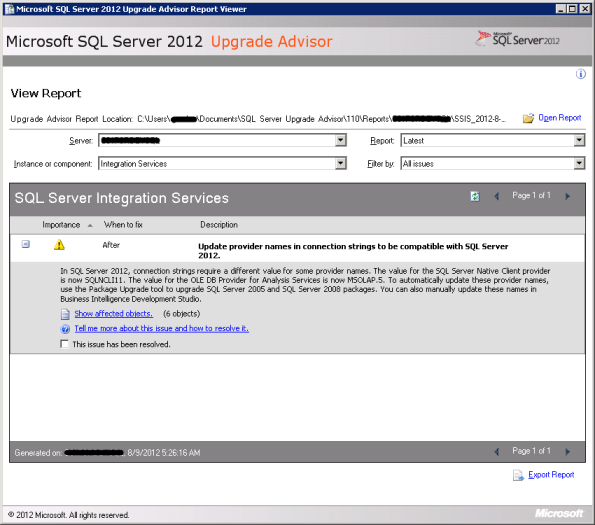
The Report Viewer tool uses this XML file generated and give you details of components that may be affected. The report provides Importance, When to fix (Before/After), Description and links to information that will help you fix or reduce the effect of the known issues, image below:
After you are done with this Analysis and checking Reports, now the time is to work and fix on issues listed in the Reports.
Other than this you also need to check Microsoft BOL and/or MSDN articles to check for Discontinued and Deprecated features, Breaking and Behavior Changes.
Check following important links:
1. SQL Server Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc707787
2. Database Engine Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143532
3. Analysis Services Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143479
4. Integration Services Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143706
5. Reporting Services Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms143251
6. Other Backward Compatibility: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280407
Columnstore Indexes in SQL Server 2012
This time the new version of SQL Server 2012 a.k.a Denali has introduced a new kind of index i.e. ColumnStore Index, which is very different from the traditional indexes. This new index differs in the way it is created, stores its table contents in specific format and provides fast retrieval of data from the new storage.
–> Before talking about ColumnStore Index, let’s first check and understand what is a ColumnStore?
ColumnStore is a data storage method that uses xVelocity technology based upon Vertipaq engine, which uses a new Columnar storage technique to store data that is highly Compressed and is capable of In-memory Caching and highly parallel data scanning with Aggregation algorithms.
Traditionally, on the other side a RowStore is the traditional and by-default way to store data for each row and then joins all the rows and store them in Data Pages, and is still the same storage mechanism for Heap and Clustered Indexes.
The ColumnStore or Columnar data format does not store data in traditional RowStore fashion, instead the data is grouped and stored as one column at a time in Column Segments.
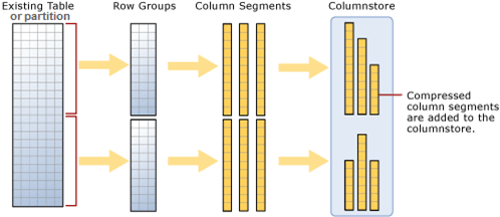
–> Here is what happens when you try to create a ColumnStore Index on a table:
1. Existing table rows are divided into multiple RowGroups, a Row-Group can contain upto 1 million rows.
2. Each column of a RowGroup is stored in its own Segment and is compressed.
3. The individual compressed Column Segments are added to the ColumnStore.
4. When new rows are inserted or existing ones are updated (in small batches, except BulkLoad) they are added to a separate Delta Store, upto a threshold of 1 million rows.
5. When a Delta-Store reaches its threshold of 1 million rows a separate process Tuple-mover invokes and closes the delta-store, compresses it & stores it into the ColumnStore index.
–> Thus, Columnstore indexes can produce faster results by doing less I/O operations by following:
1. Reading only the required columns, thus less data is read from disk to memory.
2. Heavy Column compression, which reduces the number of bytes that must be read and moved.
3. Advanced query execution technology by processing chunks of columns called batches (1000 rows) in a streamlined manner, further reducing CPU usage.
4. Stored as ColumnStore Object Pool in RAM to cache ColumnStore Index, instead of SQL Buffer Pool (for Pages)
–> Please Note: In SQL Server 2012 ColumnStore indexes has some limitations:
1. A Table (Heap or BTree) can have only one NonClustered ColumnStore Index.
2. Cannot be a Clustered Index.
3. A Table with NonClustered ColumnStore Index becomes readonly and cannot be updated.
4. Check MSDN BoL for more limitations with SQL Server 2012 version, link.