Archive
SQL Error – Windows could not start the SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER) on Local Computer (moved Master DB)
I was trying to move my Master DBs to another folder by using steps mentioned in my one of [previous blog post]. But after all steps, when I tried to Start the services I got error with following popup:
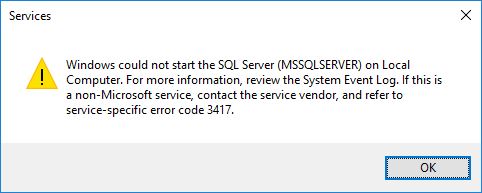
Error Description:
Windows could not start the SQL Server (MSSQLSERVER) on Local Computer. For more information, review the System Event Log. If this is a non-Microsoft service, contact the service vendor, and refer to service-specific error code 3417.
–> So, I checked the error log file and it showed the reason for error.
Default location: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Log\
…
2016-06-27 12:18:28.02 Server The service account is ‘NT Service\MSSQLSERVER’. This is an informational message; no user action is required.
2016-06-27 12:13:33.30 Server Registry startup parameters:
-d E:\SystemDatabases\Master\master.mdf
-e C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL13.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Log\ERRORLOG
-l E:\SystemDatabases\Master\mastlog.ldf
2016-06-27 12:13:33.30 Server Command Line Startup Parameters:
-s “MSSQLSERVER”
…
2016-06-27 12:13:33.41 spid5s [INFO] HkHostDbCtxt::Initialize(): Database ID: [1] ‘master’. XTP Engine version is 0.0.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.12 spid5s Starting up database ‘master’.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s Error: 17204, Severity: 16, State: 1.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s FCB::Open failed: Could not open file E:\SystemDatabases\Master\master.mdf for file number 1. OS error: 5(Access is denied.).
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s Error: 5120, Severity: 16, State: 101.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s Unable to open the physical file “E:\SystemDatabases\Master\master.mdf”. Operating system error 5: “5(Access is denied.)”.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s Error: 17204, Severity: 16, State: 1.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s FCB::Open failed: Could not open file E:\SystemDatabases\Master\mastlog.ldf for file number 2. OS error: 5(Access is denied.).
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s Error: 5120, Severity: 16, State: 101.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s Unable to open the physical file “E:\SystemDatabases\Master\mastlog.ldf”. Operating system error 5: “5(Access is denied.)”.
2016-06-27 12:18:28.13 spid5s SQL Server shutdown has been initiated
–> The above error log (in bold) tells that the service account NT Service\MSSQLSERVER does not have access to the files moved to new location.
–> So, to provide access, go to the new folder location –> Right click and select Properties –> Go to Security tab, click on Edit –> click on Add, to add the Service Account. Apply the Service Account (here in my case NT Service\MSSQLSERVER) and change the Locations to your PC, as its a local Service Account:
Give “Full Control”, and click OK on popups.
Now Start the “SQL Server” services and this time it will work.
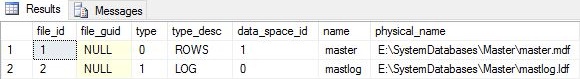
To check and confirm the new file location of Master DB, Execute following SQL query:
USE master GO SELECT * FROM sys.database_files
SQL Error – SSMS, ‘-120’ is not a valid value for property ‘Width’ or ‘Height’
Today I came across a weird error as my colleague was trying to open SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio), and it was throwing following error:
‘-120’ is not a valid value for property ‘Width’
… in the dialogue box shown below:
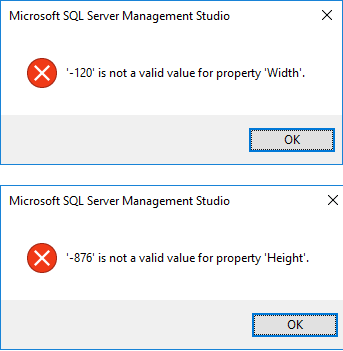
… a similar error can also occur for Height also (2nd image).
By checking the error its obvious that there is something wrong with Width or Height of SSMS Query-Editor window.
So, I went to REGEDIT (In RUN, type regedit.exe) and after navigating here n there got the location where to update this property.
Navigate to folder: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SQL Server Management Studio\13.0\
Here check the MainWindow property value (image below), it was showing: 0 451 109 -120 876 1
Change it to a positive value considering the width of your SSMS editor window, I replaced -120 with 1400

Click OK and close the Registry Editor window and re-open SSMS, it will not show this error again !
Polybase error in SQL Server 2016 : Row size exceeds the defined Maximum DMS row size, larger than the limit of [32768 bytes]
I got an email form one of my reader regarding issues while working with SQL Server 2016 and Polybase, and it is as follows:
I am able to successfully install SQL with Polybase and able to query data in Azure storage but for a table I am getting error.
I am trying to pull data by creating External Data Source connection in SQL enabled Polybase features. I am getting below error as:
Cannot execute the query “Remote Query” against OLE DB provider “SQLNCLI11” for linked server “(null)”. 107093;Row size exceeds the defined Maximum DMS row size: [40174 bytes] is larger than the limit of [32768 bytes]
With the error description its quiet evident that the External tables does not support row size more than 32768 bytes. But still I take a look online and found in Azure Documentation that this is a limitation right now with Polybase. The Azure document mentions:
Wide rows support is not supported yet, “If you are using Polybase to load your tables, define your tables so that the maximum possible row size, including the full length of variable length columns, does not exceed 32,767 bytes. While you can define a row with variable length data that can exceed this figure, and load rows with BCP, you will not be be able to use Polybase to load this data quite yet. Polybase support for wide rows will be added soon. Also, try to limit the size of your variable length columns for even better throughput for running queries.”
link: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/sql-data-warehouse-develop-table-design/
SQL Server CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY usage – MSDN TSQL forum
–> Question:
I need to see two small scenario when people should use CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY.
Please discuss the scenario with code and example.
Thanks !
–> My Answer:
CROSS APPLY acts like an INNER JOIN, and OUTER APPLY acts like a LEFT OUTER JOIN.
–> The APPLY clause (irrespective of CROSS/OUTER option) gives you flexibility to pass table’s columns as parameters to UDFs/functions while Joining while that table. It was not possible with JOINS. The function will execute for each row value passed to the UDF as parameter. But the JOIN works as a whole set.
Check the blog post on CROSS APPLY vs OUTER APPLY operators, https://sqlwithmanoj.com/2010/12/11/cross-apply-outer-apply/
–> Apart from this you can also use APPLY clause with Tables/SubQueries, like if you want to get top 5 products sold by sales persons, or get top 10 populated Cities from all States.
Check here: Using CROSS APPLY & OUTER APPLY operators with UDFs, Derived-Tables/Sub-Queries & XML data, https://sqlwithmanoj.com/2012/01/03/using-cross-apply-outer-apply-operators-with-udfs-derived-tables-xml-data/
–> Answer from Russ Loski:
First let’s start with the use for APPLY.
You would use APPLY if you need to use a column from a table as an argument in a derived table or function. For example, this query from http://blog.sqlauthority.com/2009/08/21/sql-server-get-query-plan-along-with-query-text-and-execution-count/:
SELECT cp.objtype AS ObjectType, OBJECT_NAME(st.objectid,st.dbid) AS ObjectName, cp.usecounts AS ExecutionCount, st.TEXT AS QueryText, qp.query_plan AS QueryPlan FROM sys.dm_exec_cached_plans AS cp CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_query_plan(cp.plan_handle) AS qp CROSS APPLY sys.dm_exec_sql_text(cp.plan_handle) AS st --WHERE OBJECT_NAME(st.objectid,st.dbid) = 'YourObjectName'
I need to use columns from dm_exec_cahced_plans to pass to two functions to get rows from those functions. I have to use the APPLY keyword (rather than Join) to be able to do that.
I can do the same with a derived table:
SELECT * FROM TableA outer apply ( SELECT * from TableB where TableA.id = TableB.id ) tb2
That is a horrible example (you can do the same using standard join syntax). But there are very rare circumstances where I need to use a column in a where clause in a derived table, but I can’t use a join.
The difference between CROSS APPLY and OUTER APPLY is the difference between INNER JOIN and OUTER JOIN. CROSS APPLY will only return rows where there is a row in both the first table and the second table/function, while OUTER APPLY returns a row if there is a row in the first Table even if the second table/function returns no rows.
Ref link.
SQL Server 2012: Error handling for multiple errors – MSDN TSQL forum
–> Question:
I have a stored procedure which steps through a list of transaction log backups and applies them to a DR database with NORECOVERY. As part of our DR test process, it is sometimes possible that the DR database gets ahead of the transaction log list. In this circumstance I get the error:
Msg 4326, Level 16, State 1, Line 8
The log in this backup set terminates at LSN 74000000023300001, which is too early to apply to the database. A more recent log backup that includes LSN 74000000025200001 can be restored.
Msg 3013, Level 16, State 1, Line 8
RESTORE LOG is terminating abnormally.
This is fine and I’m happy to ignore this log and move on to the next one. However there appears to be no way to catch the 4326 error. Wrapping the restore in a TRY … CATCH only identifies the 3013 error number and that could be caused by many issues that I don’t want to ignore. If my TRY … CATCH uses the THROW command, both the 4326 and 3013 errors are displayed so my session clearly has a handle to them both.
My questions are:
1. Can I catch the first error thrown?
2. Can I review all the errors thrown?
3. Can the output from THROW be captured in a variable so I can parse it?
–> Answer:
While using RAISERROR it will only catch the last error thrown, it won’t catch and return all the errors.
The new THROW keyword introduced in SQL Server 2012 returns all the errors, check this link: https://sqlwithmanoj.com/2015/02/04/capture-multiple-errors-in-try-catch-by-using-throw-statement/
But I don’t think if there is any mechanism to store both the errors returned by any script as after THROW the execution ends and control is transferred to the client.
Other than using DBCC OUTBUFFER(@@spid), you will need to parse the multiple error details spread through several rows.
Ref link.