Microsoft’s upcoming USCMO Webcasts | Digital Events
Microsoft announced their new and improved USCMO webcast programs!
The USCMO (U.S. Central Marketing Organization) team manages and optimizes programs through the customer lifecycle in order to drive business results of conversion, pipeline, and managed costs.
Each webcast will stream live with interactive Q&A and will be made available on demand.
–> Please check the webcasts below you might be interested to register:
| Webcast Title | Webcast Date | Registration URL |
| Protect Your Business Against Online Fraud | 1/20/2015 | http://aka.ms/protectblog |
| Social in the Enterprise | 1/21/2015 | http://aka.ms/enterpriseblog |
| Windows Server 2003 Migration: Hardware Modernization | 1/22/2015 | http://aka.ms/WS03blog |
| It’s a New Year, Be Ready to Adapt | 1/22/2015 | http://aka.ms/adaptblog |
| HIPAA Compliant Cloud Solutions with Microsoft BAA | 1/23/2015 | http://aka.ms/BAAblog |
| Announcing the Enterprise Cloud Suite | 1/26/2015 | http://aka.ms/suiteblog |
| Get a fresh start in 2015 with new Windows devices | 1/28/2015 | http://aka.ms/windeviceblog |
| Need fast AND affordable? Why not try SQL Server? | 1/29/2015 | http://aka.ms/SQLserverblog |
| Mobile Productivity in the Modern Workplace | 2/4/2015 | http://aka.ms/mobileblog |
| Windows Server 2003: Most Common Application Migration Concerns | 2/5/2015 | http://aka.ms/commonblog |
| Enabling Customer Insights Using Business Analytics | 2/12/2015 | http://aka.ms/customerblog |
| Windows Server 2003: Security Risk and Remediation | 2/18/2015 | http://aka.ms/remeblog |
| The Connected Workforce | 2/18/2015 | http://aka.ms/connectedblog |
| Fine Tune Your Supply Chain with Better Insight | 2/19/2015 | http://aka.ms/fineblog |
Thanks !!!
SQL Error – Index (zero based) must be greater than or equal to zero and less than the size of argument list
SQL Server version is “SQL Server 2012(SP2-CU15-GDR)(KB3194725) – 11.0.5676.0(X64)”.
An error occurred when you applied SQL Server 2012 Service Pack 3 to the current server(see attached image)
–> Summary Log
Overall summary:
Final result: The patch installer has failed to update the shared features. To determine the reason for failure, review the log files.
Exit code (Decimal): -2068774911
Exit facility code: 1201
Exit error code: 1
Exit message: Index (zero based) must be greater than or equal to zero and less than the size of the argument list.
Start time: 2018-02-22 10:40:52
End time: 2018-02-22 10:41:22
Requested action: Patch
Solution:
There can be various reasons you might be getting this issue, like a failure of a previous installation of SQL server may corrupt the registry, and this registry corruption may initiate this issue.
There seems to be no direct fix to this, so try:
– Uninstalling all the patches, and re-install them in sequence.
– Or, uninstall the whole SQL Server completely and install fresh again.
2014 in review
The WordPress.com stats helper monkeys prepared a 2014 annual report for this blog.
Here's an excerpt:
The Louvre Museum has 8.5 million visitors per year. This blog was viewed about 330,000 times in 2014. If it were an exhibit at the Louvre Museum, it would take about 14 days for that many people to see it.
What is ODS (Operational Data Store) and how it differs from Data Warehouse (DW)
I see lot of people discussing about ODS, and citing their own definitions and ideas about it. Some people also use the name as a synonym for a Data Warehouse or Factory Database. Thus, at times it becomes very difficult to tell or convince people while you are designing or architecting a DW/BI solution.
So, I thought to give some time to explain what actually an ODS is.
Simple definition: An Operational Data Store (ODS) is a module in the Data Warehouse that contains the most latest snapshot of Operational Data. It is designed to contain atomic or low-level data with limited history for “Real Time” or “Near Real Time” (NRT) reporting on frequent basis.
Detailed definifion:
– An ODS is basically a database that is used for being an interim area for a data warehouse (DW), it sits between the legacy systems environment and the DW.
– It works with a Data Warehouse (DW) but unlike a DW, an ODS does not contain Static data. Instead, an ODS contains data which is dynamically and constantly updated through the various course of the Business Actions and Operations.
– It is specifically designed so that it can Quickly perform simpler queries on smaller sets of data.
– This is in contrast to the structure of DW wherein it needs to perform complex queries on large sets of data.
– As the Data ages in ODS it passes out of the DW environment as it is.
–> Where does ODS fits in a DW/BI Architecture?
–> Classes of ODS (Types):
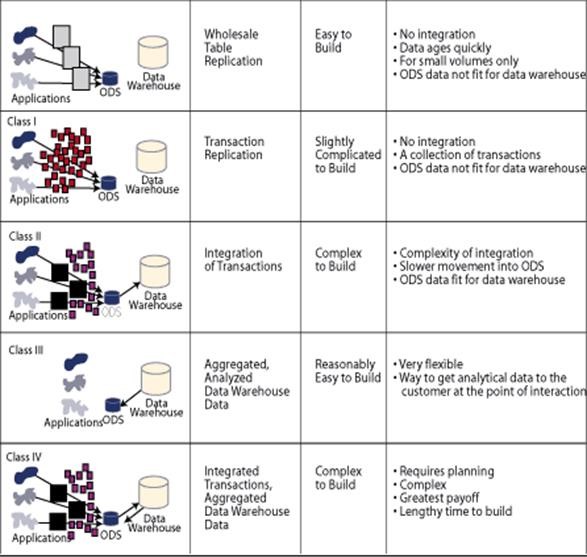
Bill Inmon defines 5 classes of ODS shown in image below:
– Class-1 ODS would simply involve Direct Replication of Operational Data (without Transformations), being very Quick.
– Whereas Class-5 ODS would involve high Integration and Aggregation of data (highly Transformed), being a very time-consuming process.
Using GROUPING SETS | SQL Server 2008 and above
In my previous posts (long back) I discussed about using [CUBE and ROLLUP] operators introduced in SQL Server 2008. I also discussed about COMPUTE & COMPUTE BY operators, but there two were removed from the SQL Server 2012 version.
Here in this post I’ll talk about GROUPING SETS (few days back my friend asked me about this and I thought its better to document this here).
Just like CUBE and ROLLUP, GROUPING SETS are used to GROUP and calculate Sub Totals and Totals within a set of records. Compared to ROLLUP with GROUPING SETS you have more flexibility to show Sub Totals on selected columns.
-- ROLLUP SELECT class, section, rollno, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable GROUP BY class, section, rollno WITH ROLLUP
Output:
class section rollno sum
HighSchool a 1 80
HighSchool a 2 70
HighSchool a 3 80
HighSchool a NULL 230
HighSchool b 4 90
HighSchool b 5 90
HighSchool b 6 50
HighSchool b NULL 230
HighSchool NULL NULL 460
Intermediate a 1 60
Intermediate a 2 50
Intermediate a 3 80
Intermediate a NULL 190
Intermediate b 4 90
Intermediate b 5 50
Intermediate b 6 70
Intermediate b NULL 210
Intermediate NULL NULL 400
NULL NULL NULL 860
–> Now, if you want to just Sub Total on Class level, you just need to use GROUPING SET operator like this:
-- GROUPING SETS on selective columns SELECT class, section, rollno, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ( (class, section, rollno) ,(class) )
This will give you more controlled Sub Totaling and grouping on selected columns:
Output:
class section rollno sum
HighSchool a 1 80
HighSchool a 2 70
HighSchool a 3 80
HighSchool b 4 90
HighSchool b 5 90
HighSchool b 6 50
HighSchool NULL NULL 460
Intermediate a 1 60
Intermediate a 2 50
Intermediate a 3 80
Intermediate b 4 90
Intermediate b 5 50
Intermediate b 6 70
Intermediate NULL NULL 400
–> You can also get the same output like ROLLUP operator, but you have to provide columns in following groups:
-- GROUPING SETS SELECT class, section, rollno, sum(marks) [sum] FROM #tempTable GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ( (class, section, rollno) ,(class, section) ,(class) ,() )
Note: You can also use GROUPING SETS with combination of ROLUP and/or CUBE operators, check more on regarding this on MS BoL, here.
–> Grouping Sets equivalent for SQL Server 2005 and below, check here.