DB Basics – Integrity Constraints in a Database (SQL Server)
Integrity constraints are used to ensure accuracy and consistency of data in a relational database. Data integrity allows to define certain data quality requirements that the data in the database needs to meet. If a user tries to insert data that doesn’t meet these requirements, the RDBMS will not allow so.
A Constraint is a property assigned to a column or the set of columns in a table that prevents certain types of inconsistent data values from being placed in the column(s). Constraints are used to enforce the data integrity. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data in the database.
CONSTRAINT = The threat or use of force to prevent, restrict, or dictate the action or thought of others.
–> There are 7 types of Constraints and they are grouped in to 4 types:
| A. ENTITY INTEGRITY | 1. Primary Key | blog post | video |
| 2. Unique Key | video | ||
| B. REFERENTIAL INTEGRITY | 3. Foreign Key | blog post | video |
| C. DOMAIN INTEGRITY | 4. NOT NULL | blog post | video |
| 5. DEFAULT | |||
| 6. CHECK | |||
| D. USER DEFINED INTEGRITY | 7. RULES | blog post | video |
–> Check the video with discussion on all these Constraints:
CUBE, ROLLUP, COMPUTE, COMPUTE BY, GROUPING SETS
The CUBE and ROLLUP operators are useful in generating reports that contain subtotals and totals. There are extensions of the GROUP BY clause.
–> Difference b/w CUBE and ROLLUP:
– CUBE generates a result set that shows aggregates for all combinations of values in the selected columns.
– ROLLUP generates a result set that shows aggregates for a hierarchy of values in the selected columns.
Let’s check this by a simple example:
select 'A' [class], 1 [rollno], 'a' [section], 80 [marks], 'manoj' stuName into #tempTable UNION select 'A', 2, 'a', 70 ,'harish' UNION select 'A', 3, 'a', 80 ,'kanchan' UNION select 'A', 4, 'b', 90 ,'pooja' UNION select 'A', 5, 'b', 90 ,'saurabh' UNION select 'A', 6, 'b', 50 ,'anita' UNION select 'B', 1, 'a', 60 ,'nitin' UNION select 'B', 2, 'a', 50 ,'kamar' UNION select 'B', 3, 'a', 80 ,'dinesh' UNION select 'B', 4, 'b', 90 ,'paras' UNION select 'B', 5, 'b', 50 ,'lalit' UNION select 'B', 6, 'b', 70 ,'hema' select class, rollno, section, marks, stuName from #tempTable
Output:
class rollno section marks stuName
A 1 a 80 manoj
A 2 a 70 harish
A 3 a 80 kanchan
A 4 b 90 pooja
A 5 b 90 saurabh
A 6 b 50 anita
B 1 a 60 nitin
B 2 a 50 kamar
B 3 a 80 dinesh
B 4 b 90 paras
B 5 b 50 lalit
B 6 b 70 hema
–> WITH ROLLUP:
select class, section, sum(marks) [sum] from #tempTable group by class, section with ROLLUP
Output:
class section sum
A a 230
A b 230
A NULL 460 -- 230 + 230 = 460
B a 190
B b 210
B NULL 400 -- 190 + 210 = 400
NULL NULL 860 -- 460 + 400 = 860
–> WITH CUBE:
select class, section, sum(marks) [sum] from #tempTable group by class, section with CUBE
Output: class section sum A a 230 A b 230 A NULL 460 -- 230 + 230 = 460 B a 190 B b 210 B NULL 400 -- 190 + 210 = 400 NULL NULL 860 -- 460 + 400 = 860 NULL a 420 -- 230 + 190 = 420 NULL b 440 -- 230 + 210 = 440
–> COMPUTE & COMPUTE BY: (this feature is no longer supported and discontinued with SQL Server 2012 and next versions)
A COMPUTE BY clause allows you to see both detail and summary rows with one SELECT statement. You can calculate summary values for subgroups, or a summary value for the whole result set.
The COMPUTE clause takes the following information:
– The optional BY keyword. This calculates the specified row aggregate on a per column basis.
– A row aggregate function name. This includes SUM, AVG, MIN, MAX, or COUNT.
– A column upon which to perform the row aggregate function.
select class, section, marks from #tempTable COMPUTE SUM(marks), AVG(marks) select class, section, marks from #tempTable order by class COMPUTE SUM(marks), AVG(marks) by class select class, section, marks from #tempTable order by class, section COMPUTE SUM(marks), AVG(marks) by class, section
Final Cleanup, drop the temp tables:
drop table #tempTable
–> GROUPING SETS:
SQL Server 2008 has a new GROUPING SETS operator which can generate the same result set as that generated by using a simple GROUP BY, ROLLUP, or CUBE operator.
–> Grouping Sets for SQL Server 2008 and above, check here.
–> Grouping Sets equivalent for SQL Server 2005 and below, check here.
>> Check & Subscribe my [YouTube videos] on SQL Server.
Query Excel file source through Linked Server
In previous post we saw how to setup a Linked Server for MySQL Database. Now lets go with other data sources. Excel files are the most important source of data and report management in a particular department.
When you need to do some query on Excel data, one way is to use Import/Export wizard, push the excel contents to SQL Server and then query on SQL Server DB. Another and easy way is to create a Linked Server to Excel file and query directly the Excel file itself.
You just need to create the Excel file and execute the following SQL Statements below:
–> For Excel 2003 format:
USE MSDB GO EXEC sp_addLinkedServer @server= 'XLS_NewSheet', @srvproduct = 'Jet 4.0', @provider = 'Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0', @datasrc = 'C:\Manoj_Advantage\NewSheet.xls', @provstr = 'Excel 5.0; HDR=Yes'
– Now, query your excel file in two ways:
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY (XLS_NewSheet, 'Select * from [Sheet1$]') SELECT * FROM XLS_NewSheet...[Sheet1$]
–> For Excel 2007 format:
USE MSDB GO EXEC sp_addLinkedServer @server= 'XLSX_NewSheet', @srvproduct = 'ACE 12.0', @provider = 'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0', @datasrc = 'C:\Manoj_Advantage\NewSheet.xlsx', @provstr = 'Excel 12.0; HDR=Yes'
– Now, query your excel file in two ways:
SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY (XLSX_NewSheet, 'Select * from [Sheet1$]') SELECT * FROM XLSX_NewSheet...[Sheet1$]
Note: If your excel file don’t have headers, then set HDR=No
You may need to execute the following SQL Statements to configure the Linked Server initially:
USE MSDB GO sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1 GO RECONFIGURE WITH OverRide GO sp_configure 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', 1 GO RECONFIGURE WITH OverRide GO
>> Check & Subscribe my [YouTube videos] on SQL Server.
Creating Linked Server in SQL Server
Linked Servers provides access to external datasources be it another databases like Oracle, MySQL, or Excel files.
Advantages:
– Remote server access.
– The ability to issue distributed queries, updates, commands, and transactions on heterogeneous data sources across the enterprise.
– The ability to address diverse data sources similarly.
MSDN Links on Linked Servers:
Info: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188279(v=SQL.90).aspx
Configure: http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa213778(SQL.80).aspx
My idea here is to query MySQL tables in MS SQL Server as I’m more comfortable with MS SQL queries and semantics. I don’t know if or how I can use Ranking functions, case statements, etc in MySQL DB. Plus I’m also not comfortable in writing queries in DOS like editor or any other freeware tool.
Linked Server to MySQL:
Before creating a Linked Server for MySQL you need to install the MySQL ODBC connector.
Download MySQL ODBC Client: http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/odbc/
Now we need a DSN that will act as a bridge between for creating the Linked Server:
Create a System DSN:
– On Control Pannel -> Admin Tools -> Data Sources (ODBC), Select System DSN tab, click ADD, Selct “MySQL ODBC 3.51 Driver”, Click Finish.
– A new pop-up will come up, “Connector/ODBC 3.51.27 – Configure Data Source Name”.
– On Login Tab: Set fields, Click Test.
– On Advanced Tab, go to following tabs and check the options:
– Flag1: Return Matching Rows, Allow Big Results, Use Compressed Protocol, Change BIGINT columns to Int, Safe
– Flag2: Don”t Prompt Upon Connect, Ignore # In Table Name
– Flag3: Return Table Names for SQLDescribeCol, Disable Transactions
– Click “OK”
Create a New Linked Server:
– On SSMS under Object Explorer go to “Server Objects” -> “Linked Servers”, Richt Click and select “New Linked Server”
– Set an appropriate name on “Linked Server”, like: MYSQL_LINK
– Server Type = Select “Other Data Source” radio button.
– Set Provider = Microsoft OLE DB Provider for ODBC Drivers
– Set the “Product Name” & “Data Source” field you set on configuring the DSN.
This can also be setup by following SQL statements:
-- Create New Linked Server EXEC sp_addlinkedserver @server = 'MYSQL_LINK', @srvproduct = 'MySQLDatabase', @provider = 'MSDASQL', @datasrc = 'MySQLKayako' -- Pull list of all Servers select * from sys.servers EXEC sp_linkedservers -- Drop the Linked Server EXEC sp_dropserver 'MYSQL_LINK'
Now you can query the tables and other objects of MySQL database by using OPENQUERY function as shown below:
-- Select a table or view SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(MYSQL_LINK, 'select * from MySQL_Table') -- Execute a function SELECT * FROM OPENQUERY(MYSQL_LINK, 'EXEC MySQL_Proc param1, param2')
OPENQUERY() also helps in selecting a Stored Procedure result just like a table.
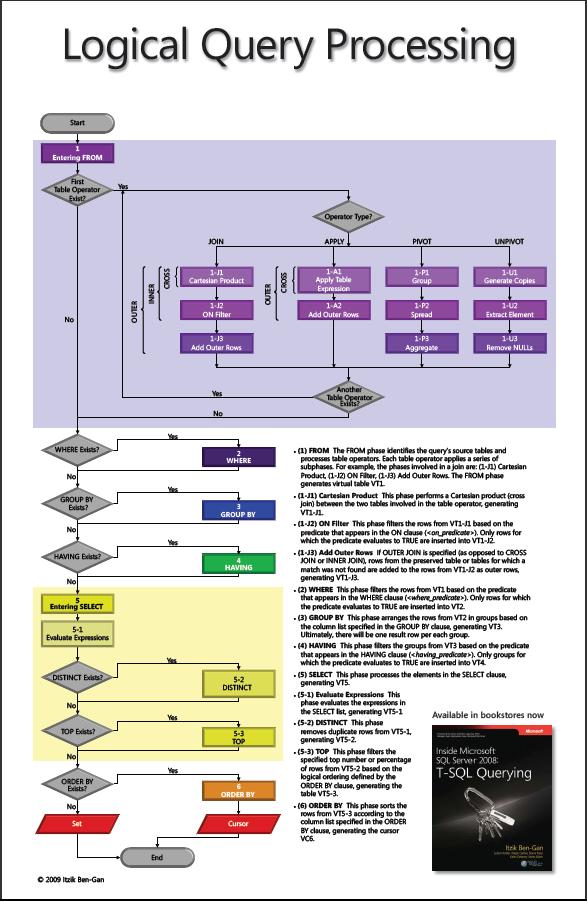
SQL Logical Query Processing Order
–>Logical Query-processing step numbers:
(5) SELECT (5-2) DISTINCT (7) TOP(<top_specification>) (5-1) <select_list> (1) FROM (1-J) <left_table> <join_type> JOIN <right_table> ON <on_predicate> | (1-A) <left_table> <apply_type> APPLY <right_input_table> AS <alias> | (1-P) <left_table> PIVOT(<pivot_specification>) AS <alias> | (1-U) <left_table> UNPIVOT(<unpivot_specification>) AS <alias> (2) WHERE <where_predicate> (3) GROUP BY <group_by_specification> (4) HAVING <having_predicate> (6) ORDER BY <order_by_list> (7) OFFSET <offset_specs> ROWS FETCH NEXT <fetch_specs> ROWS ONLY;
–> Logical step sequence of a Query:
1. FROM / JOIN/ APPLY/ PIVOT/ UNPIVOT
2. WHERE
3. GROUP BY
4. HAVING
5. SELECT list/ DISTINCT
6. ORDER BY
7. TOP/ OFFSET-FETCH
–> Flow diagram representing logical query-processing: