Archive
New built-in function STRING_AGG() with option “WITHIN GROUP” – SQL Server 2017
In one of my [previous post] I discussed about a new function STRING_SPLIT() introduced in SQL Server 2016, which splits a Sentence or CSV String to multiple values or rows.
Now with the latest CTP 1.x version of SQL Server vNext (I’m calling it “SQL Server 2017”) a new function is introduced to just do its reverse, i.e. Concatenate string values or expressions separated by any character.
The STRING_AGG() aggregate function takes all expressions from rows and concatenates them into a single string in a single row.
It implicitly converts all expressions to String type and then concatenates with the separator defined.
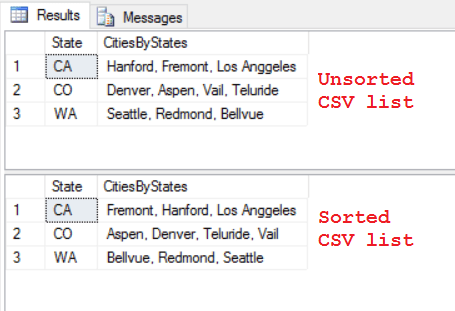
–> In the example below I’ll populate a table with States and Cities in separate rows, and then try to Concatenate Cities belonging to same States:
USE tempdb GO CREATE TABLE #tempCityState ( [State] VARCHAR(5), [Cities] VARCHAR(50) ) GO INSERT INTO #tempCityState SELECT 'CA', 'Hanford' UNION ALL SELECT 'CA', 'Fremont' UNION ALL SELECT 'CA', 'Los Anggeles' UNION ALL SELECT 'CO', 'Denver' UNION ALL SELECT 'CO', 'Aspen' UNION ALL SELECT 'CO', 'Vail' UNION ALL SELECT 'CO', 'Teluride' UNION ALL SELECT 'WA', 'Seattle' UNION ALL SELECT 'WA', 'Redmond' UNION ALL SELECT 'WA', 'Bellvue' GO SELECT * FROM #tempCityState
State Cities
CA Hanford
CA Fremont
CA Los Anggeles
CO Denver
CO Aspen
CO Vail
CO Teluride
WA Seattle
WA Redmond
WA Bellvue
–> To comma separate values under a single row you just need to apply the STRING_AGG() function:
SELECT STRING_AGG(Cities, ', ') as AllCities FROM #tempCityState -- Use "WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY ...)" clause to concatenate them in an Order: SELECT STRING_AGG(Cities, ', ') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY Cities) as AllCitiesSorted FROM #tempCityState

–> Now to Concatenate them by States, you just need to group them by the State, like any other aggregate function:
SELECT State, STRING_AGG(Cities, ', ') as CitiesByStates FROM #tempCityState GROUP BY State -- Use "WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY ...)" clause to concatenate them in an Order: State, STRING_AGG(Cities, ', ') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY Cities) as CitiesByStatesSorted FROM #tempCityState GROUP BY State
You can check more about STRING_AGG() on MSDN.
SQL DBA – Quickly Clone a Database in SQL Server (2016 SP1 & 2014 SP2) with DBCC CLONEDATABASE command
Have you ever been in a similar situation where your PROD database size is in GBs or TBs, and for a code-release validation or some performance-fix you need to restore it on an Dev or Test server? You know that taking backup & restore will take lot of time, but you have no other option.
We also face this many a times as our PROD database size ranges from 500 GB to 1-2 TB, and we end up waiting 4-5 hrs in this activity.
There are even third party tools, but they also take good time and have their own pros & cons.
Now SQL Server brings a new feature with SQL Server 2016 SP1 & 2014 SP2, i.e. DBCC CLONEDATABASE, to create a new database clone of an existing database within seconds. The new cloned database created is ReadOnly, with no data, but with Statistics.
With DBCC CLONEDATABASE feature you can generate a clone of a database in order to investigate a performance issue related to a Query or Workload.
Note: As best practice suggested by Microsoft product team this clone Database is not supposed to remain in PROD database, but can be moved to a Dev or Test box for further troubleshooting and diagnostic purposes.
–> Syntax:
DBCC CLONEDATABASE (source_db_name, target_clone_db_name)
[WITH [NO_STATISTICS][,NO_QUERYSTORE]]
–> The above statement creates Clone of the source database in following operations:
1. Validate the source database.
2. Get S lock for the source database.
3. Create snapshot of the source database.
4. Create an empty database by inheriting from “model” database, and using the same file layout as the source but with default file sizes as the “model” database.
5. Get X lock for the clone database.
6. Copies the system metadata from the source to the destination database.
7. Copies all schema for all objects from the source to the destination database.
8. Copies statistics for all indexes from the source to the destination database.
9. Release all DB locks.
–> Now let’s create a Clone Database on AdvantureWorks database:
-- With Stats
DBCC CLONEDATABASE ('AdventureWorks2014', 'AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB')
Message:
Database cloning for ‘AdventureWorks2014’ has started with target as ‘AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB’.
Database cloning for ‘AdventureWorks2014’ has finished. Cloned database is ‘AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB’.
Database ‘AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB’ is a cloned database. A cloned database should be used for diagnostic purposes only and is not supported for use in a production environment.
DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
–> I’ll create one more Clone Database without Stats:
-- Without Stats
DBCC CLONEDATABASE ('AdventureWorks2014', 'AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB_No_Stats')
WITH NO_STATISTICS, NO_QUERYSTORE
–> Let’s check the file size of all 3 Databases:
– The 1st image shows the size of original AdventureWorks2014 database i.e. 207 MB
– And 2nd and 3rd shows the size of other two Clone Databases i.e. just 16 MB.
–> Now we will check the Execution Plans of a query on all these three databases:
-- Check Execution plan on below T-SQL query in all 3 databases: SELECT P.BusinessEntityID, P.Title, P.FirstName, P.MiddleName, P.LastName, E.BirthDate, E.Gender, E.HireDate, E.JobTitle, E.MaritalStatus, D.Name FROM [Person].[Person] P INNER JOIN [HumanResources].[Employee] E ON E.BusinessEntityID = P.BusinessEntityID CROSS APPLY ( SELECT TOP 1 DepartmentID FROM [HumanResources].[EmployeeDepartmentHistory] DH WHERE DH.BusinessEntityID = E.BusinessEntityID ORDER BY StartDate DESC) EDH INNER JOIN [HumanResources].[Department] D ON D.DepartmentID = EDH.DepartmentID
– On executing the above query on original AdventureWorks2014 database & AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB it shows same execution plan, like it shows:
1. Hash Match operator
2. 72% cost on Person PK
3. 18% cost on EmployeeDepartmentHistory PK

(click on the image to expand)
– But on executing the same query on AdventureWorks2014_CloneDB_No_Stats it shows different execution plan, here it shows:
1. Nested Loop operator
2. 92% cost on Person PK
3. 5% cost on EmployeeDepartmentHistory PK

(click on the image to expand)
Microsoft released SQL Server vNext (2017) – New features and enhancements in CTP 1.x
On 16th Nov 2016 Microsoft announced the first Community Test Preview (CTP 1.0) of SQL Server vNext that will run both on Windows & Linux. Not only Linux, but it will be supported on Docker, and macOS (via Docker) too.
For now I’m calling the vNext version as SQL Server 2017. (2018 is not called officially, I’m calling it just to avoid any confusion 🙂 )
This announcement was along with the release of SQL Server 2016 SP1, and the vNext version also supports features added in SQL Server 2016 SP1.
–> Download vNext bits:
To download the SQL Server vNext you can Register and Download the Full version or Free evaluation version (180 days).
Or, directly download the ISO (~2 GB): SQLServerVnextCTP1-x64-ENU.iso
–> Check version and SQL build:
select @@version
Microsoft SQL Server vNext (CTP1) – 14.0.1.246 (X64)
Nov 1 2016 23:24:39
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation
Developer Edition (64-bit) on Windows 10 Enterprise 6.3 (Build 14393: ) (Hypervisor)
–> New Features & Enhancements:
>> Database Engine:
1. All new features in SQL Server 2016 SP1.
2. New compatibility level 140.
3. Improvements to the way incremental statistics update thresholds are computed.
4. New DMVs added:
– sys.dm_exec_query_statistics_xml added, to get query execution plan for in-flight requests.
– sys.dm_os_host_info, to provide operating system information for both Windows and Linux.
5. Enhancements to In-Memory Tables & SPs:
– Can now use sp_spaceused, sp_rename, CASE, TOP (N) WITH TIES
– More than 8 indexes
6. Clustered Columnstore Indexes now support LOB columns (nvarchar(max), varchar(max), varbinary(max)).
7. New STRING_AGG() aggregate function has been added.
8. Database roles are created with R Services for managing permissions associated with packages.
9. New Japanese collations are added.
– Features added in CTP 1.1
10. Memory-optimized tables and indexes now support computed columns
– Full support for JSON functions
– and CHECK constraints
– Natively compiled modules now support the CROSS APPLY operator
12. New string functions CONCAT_WS, TRANSLATE, and TRIM are added.
– and the WITHIN GROUP clause is now supported for the STRING_AGG function.
– Features added in CTP 1.2
13. Online index build and rebuild support for non-clustered Columnstore indexes.
14. Support for SUSE Linux Enterprise Server v12 SP2
15. SQL Server Early Adoption Program (EAP), msdn blog on EAP
– Features added in CTP 1.3
16. Full text search, now available for all supported Linux distros
17. Resumable online index rebuilds
18. Temporal Tables Retention Policy
19. Indirect checkpoint performance improvements
20. Online non-clustered columnstore index buill and rebuild support added
21. Availability Groups enhancements:
– Cluster-less Availability Groups support added
– Minimum Replica Commit Availability Groups setting
– Availability Groups can now work across Windows-Linux to enable cross-OS migrations and testing
22. New DMV sys.dm_db_stats_histogram, for examining statistics
23. 5 new dynamic management views to return information about Linux process:
– sys.dm_linux_proc_all_stat
– sys.dm_linux_proc_cpuinfo
– sys.dm_linux_proc_meminfo
– sys.dm_linux_proc_sql_maps
– sys.dm_linux_proc_sql_threads
>> SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS):
1. 1400 Compatibility level for tabular models.
2. Modern Get Data query and import data features for tabular models.
3. Support for ragged hierarchies with the new Hide Members property.
4. Support for drillthrough by using Detail Rows. This includes the Default Detail Rows expression property and DETAILROWS DAX function.
5. Table-level security, restricts user permissions on table data and table names.
6. New DAX IN function.
7. Encoding hints, an advanced feature used to optimize processing (data refresh) of large in-memory Tabular models.
>> SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS):
– Support Scale Out of SSIS: to run SSIS on multiple machines. With Scale Out Master and Workers, packages can be distributed to execute on different Workers automatically. Check more details here in MSDN.
>> SQL Server R support: Check full details here in MSDN.
–> For new Features released in CTP 2.0 check here.
–> Download & Install SQL Server vNext & SSMS:
–> References:
>> SQL Server vNext Release Notes
Now “CREATE OR ALTER” Stored Procedure, Function, View, Trigger with SQL Server 2016
SQL Server 2016 release was packed with lot of new features, and I tried to cover most of them, [check here]. This includes some of the major new features like, Polybase, Temporal Tables, JSON support, Stretch DB, Row Level Security, Dynamic data Masking, etc. are very unique to the other Database systems in competition.
But Microsoft’s SQL Server team also keeps on adding few features in every release which were already there in other Database systems, so that developers could use those and make their life easier, like the new IF EXISTS option with DROP & ALTER statements I already discussed in my [previous post].
Now, with the recent Service Pack 1, one more feature has been added, which developers (mainly from the Oracle background) were missing from long time, and that is CREATE OR ALTER option while creating programming modules, like:
1. Stored Procedures (SP)
2. Functions (UDFs)
3. Views
4. Triggers
–> Now you can create a new Stored Procedure without checking its existence, simply by using the new CREATE OR ALTER option, like below:
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE dbo.spgetEmployeeDetails @EmpID INT AS BEGIN SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName FROM Person.Person WHERE BusinessEntityID = @EmpID END GO
… you can execute the above code multiple times and it won’t fail. First time this CREATEs the SP, next time it will ALTER it.
–> Previously you need to add an IF EXISTS() condition to check if the SP already exists or not. If exists then drop and then create a new SP, like:
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.ROUTINES WHERE ROUTINE_NAME = 'spgetEmployeeDetails') DROP PROCEDURE dbo.spgetEmployeeDetails GO CREATE PROCEDURE dbo.spgetEmployeeDetails @EmpID INT AS BEGIN SELECT BusinessEntityID, Title, FirstName, MiddleName, LastName FROM Person.Person WHERE BusinessEntityID = @EmpID END GO
SQL Server 2016 1st Service Pack (SP1) is out (download, new features & enhancements)
Almost 6 months back i.e. on 1st June 2016 Microsoft released SQL Server 2016 RTM, i.e. full and final version, which you can [check and download here].
Yesterday (i.e. 16-Nov-2016) Microsoft released the 1st Service Pack (SP1) of SQL Server 2016.
–> Download:
To download the SQL Server 2016 SP1 you can Register and Download the Full version or Free evaluation version (180 days).
… or you can Download the new Setup utility here, which provides you option to do a Basic or Custom installation, or download the ISO or CAB file (~2.5 GB).
… or you can also just download the Service Pack (SP1) (~550 MB), instead of the whole Setup (~2.5 GB).
–> What’s new SP1:
1. Features which were only available in Enterprise edition are now enabled in Standard, Web, Express, and LocalDB editions, link.
2. List of Bugs and issues fixed, link.
3. CREATE OR ALTER syntax for Stored Procedures, Views, Functions, and Triggers.
4. DBCC CLONEDATABASE (source_database_name, target_database_name), with optional WITH NO_STATISTICS, NO_QUERYSTORE. Creates a duplicate database by cloning Schema, metadata and statistics, without the data.
5. OPTION (USE HINT(‘hint1’, ‘hint2’)), support for a more generic query hinting is added, link.
6. Post this Service Pack (SP1) Parallel INSERTs in INSERT..SELECT to local temporary tables is disabled by default and will require TABLOCK hint for parallel insert to be enabled.
7. New DMVs are added, and some enhanced:
– sys.dm_exec_valid_use_hints to list hints
– sys.dm_exec_query_statistics_xml to return showplan XML transient statistics
– sys.dm_db_incremental_stats_properties to check incremental statistics for the specified table
– New column instant_file_initialization_enabled is added to sys.dm_server_services, to allow DBAs to programmatically identify if Instant File initialization (IFI) is in effect at the SQL Server service startup.
– New column estimated_read_row_count is added to sys.dm_exec_query_profiles
– New columns sql_memory_model and sql_memory_model_desc are added to sys.dm_os_sys_info, to provide information about the locking model for memory pages, and to allow DBAs to programmatically identify if Lock Pages in Memory (LPIM) privilege is in effect at the service startup time.