Archive
SQL Server 2016 Certification Path
Microsoft has made few changes to its Certification path for the new version of SQL Server i.e. SQL Server 2016.
And with this post I’m trying to collate and put all exams and certifications in concise and clear manner. Would be happy to accept any comments, changes and suggestions !!!
–> The MCSA i.e. “Microsoft Certified Solution Associate” level now contains the new “MCSA: SQL Server 2016” certification, and this replaces the older “MCSA: SQL Server 2012/14” one.
–> And the top MCSE i.e. “Microsoft Certified Solutions Expert” level now contains the new “MCSE: Data Management and Analytics” certification. This also replaces the following 2 existing certifications (but retains the underlying exams to earn this MCSE level, which I’ve explained below):
– MCSE: Data Platform
– MCSE: Business Intelligence

–> Here are the details of exams at both the levels.
Level 1. “MCSA: SQL Server 2016”: Now to earn this level you need to give either of the following certifications:
1. MCSA: SQL 2016 Database Development certification
– Exam [70-761], Querying Data with Transact-SQL [check details here]
– Exam [70-762], Developing SQL Databases
2. MCSA: SQL 2016 Database Administration certification
– Exam [70-764], Administering a SQL Database Infrastructure
– Exam [70-765], Provisioning SQL Databases
3. MCSA: SQL 2016 Business Intelligence Development certification
– Exam [70-767], Implementing an SQL Data Warehouse
– Exam [70-768], Developing SQL Data Models
Level 2. “MCSE: Data Management and Analytics”: Now to earn this level you need to first get an MCSA on either of the above 3 certifications, or “MCSA: Data Science”. Then need to pass anyone of the below exam:
– Exam [70-473], Designing and Implementing Cloud Data Platform Solutions
– Exam [70-475], Designing and Implementing Big Data Analytics Solutions
– Exam [70-464], Developing Microsoft SQL Server Databases
– Exam [70-465], Designing Database Solutions for Microsoft SQL Server
– Exam [70-466], Implementing Data Models and Reports with Microsoft SQL Server
– Exam [70-467], Designing Business Intelligence Solutions with Microsoft SQL Server

SSDT – OLE DB or ODBC error: Login failed for user ‘DOMAIN\ComputerName $’ 28000
My colleague was working on a Tabular Model project and while working with the Tables so that they can be deployed to the Cube on Analysis Server, he was getting a weird error. The authentication was failing and in error message it was showing the computer name instead of his actual user name, suffixed with a $ sign.
Failed to save modifications to the server.
Error returned: ‘OLE DB or ODBC error: Login failed for user ‘DOMAIN\ComputerName$‘.; 28000.
A connection could not be made to the data source with the name of ‘CubeConnectionName’.
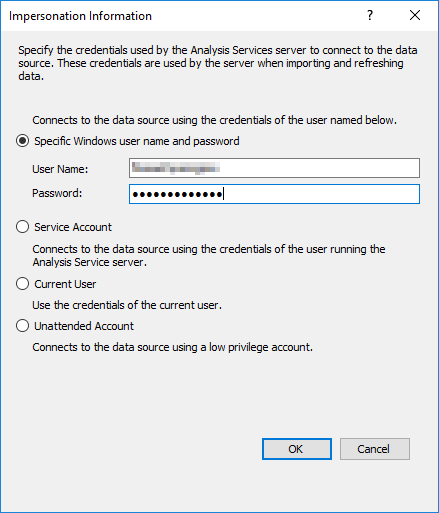
By looking at the above error it seemed that somewhere the authentication is being overridden by some setting. So after some research I found that in Data Source section there is Impersonation setting which can be set to a specific user, service account, current user or an unattended account.
–> Here is the resolution:
1. On Tabular Model Explorer go to the Project and expand Data Sources.
2. Here right click on the connection and click on Edit Data Source, or just double click on it.
3. Click on the Impersonation… button and check what option is selected.
… I found that the selection was defaulted to Service Account, and as my SSAS (Analysis Services) was running under the DOMAIN\ComputerName account which gets sets while installing SSAS. And as it does not have sufficient privileges or access rights, it fails to connect to the Database Server. Thus you need to check impersonation and provide an account which has access to the Database Server.
4. Change the selection from “Service Account” to “Specific Windows user name and password”, and apply the user name and password.
5. Click OK and Save the settings.
6. Now go again to the Table Properties and click on Refresh Preview button and click OK.
Which SQL Server Certification should I take: 98-364, 70-461 or 70-761 ? – MSDN TSQL forum
–> Question:
I just started learning SQL Server, and I want to get certified, I checked internet, but I got confused.
There is exam 98-364, 70-461, 70-761, and i want to get MCSA in SQL
could some one explain to me what should i do …
–> My Answer:
>> MCSA or Microsoft Certified Solutions Associate in SQL Server can be earned on following areas with respective exams:
– Database Development (761, 762)
– Database Administration (764, 765)
– Business Intelligence (767, 768)
>> Exam 98-364 is to get Microsoft Technology Associate (MTA) certification. It is the most basic exam that focuses just on basic SQL, and is for people new to technology, who need to validate their knowledge of fundamental concepts before moving on to more advanced certifications. This exam covers:
1. RDBMS, DBMS concepts and terms, like Normanization, PK, FK, etc.
2. Plain SQL querying knowledge, like DDL, DML, etc. and indexes.
3. Simple DBA stuff, like security, backup/restore, etc.
Link: https://www.microsoft.com/en-in/learning/exam-98-364.aspx
>> Exam 70-761 is also an advanced exam which is based upon SQL Server 2016, which is the latest version of SQL Server as of today. To earn MCSA you have to take 70-762 exam as well as mentioned above, check this link for MCSA SQL Server 2016: https://www.microsoft.com/en-in/learning/mcsa-sql-2016-certification.aspx
>> Exam 70-461 is also an advance level exam but now older based upon SQL Server 2012 or 2014. Check this link for MCSA SQL Server 2012/2014: https://www.microsoft.com/en-in/learning/mcsa-sql-certification.aspx
Please note: Exam 98-364 is not required here, and as mentioned above its just to make sure you have knowledge in working with basic SQL Querying.
Ref link.
This blog just crossed 2 million hits – Thanks !!!
Today this blog crossed 2 million hits !!!
Last time the first [1 million] milestone was achieved at June 2015, and it took almost 5 years to achieve this.
This time in Jan 2017 the 2 million milestone got achieved in just 1 year 6 months (to get extra 1 million hits).
–> Here is the stats of “Year by Year” hits:
I would like to thank all my readers and visitors for your continued support, comments and suggestions !!!
Connect SQL Server on Linux with SSMS from a Windows machine
In [previous post] we saw how to install & setup SQL Server on Linux. We used PuTTY to connect to the Linux Azure VM and query SQL Server there.
Here in this post we will try to connect to SQL Server on Linux via SSMS from a Windows machine.
So to connect remotely to SQL Server on an Azure VM, you have to configure an inbound rule on the network security group. The rule allows traffic on the port on which SQL Server listens (default is 1433).
–> Setup Inbound Rule:
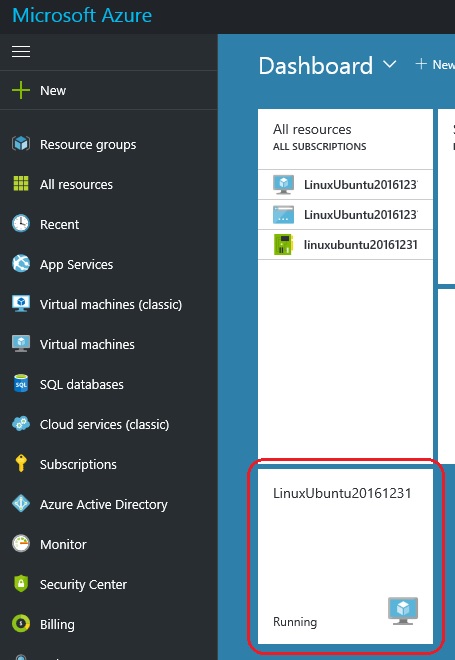
1. You need to go to portal.azure.com and login with your credentials. On the Dashboard you will see your Linux VM as shown below:
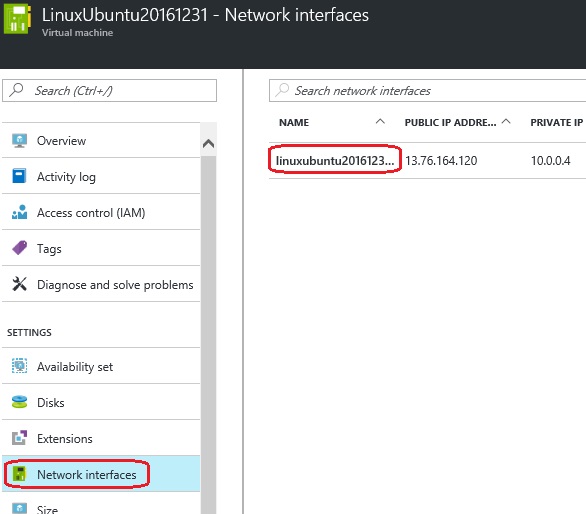
2. Click on the Linux VM widget, it will open up and list out the Settings, click on Network Interfaces, and select the available Network Interface from the list.
3. Now click on the Network Security Group:
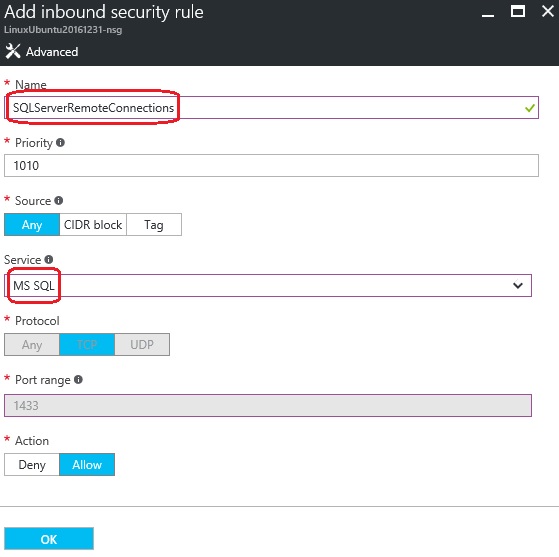
4. On the Network Security Group page, select the Inbound security rules, and click on the “+” button create new for SQL Server:
5. On the Add inbound security rule page, provide a name to this rule, select “MS SQL” under Service drop-down, and click OK:
–> Connect using SSMS:
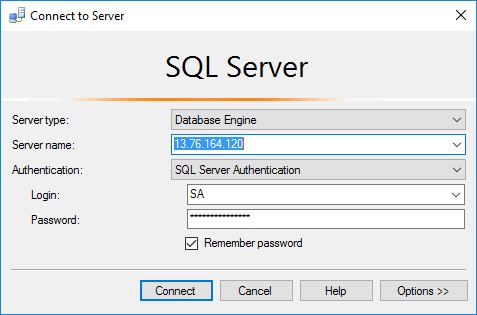
6. Now from any Remote machine or even you PC which has SSMS installed and have internet connection, try connecting the SQL Server Linux Instance:
– Server Name: provide the IP address of the Linux VM (you can get it by opening the “Linux VM widget” and clicking on “Connect” button at top)
– Authentication: should be SQL Server Authentication
– Login: “SA”
– Password: apply the same password that you set it up while Configuring SQL Server on Linux.
7. On successful authentication you will see the Object Explorer showing the SQL instance that’s running on a Linux machine. On a glance you can’t make out any difference b/w a Linux SQL instance or a Windows SQL instance.
Thus I executed the SELECT @@version statement which shows the SQL Server version and on which Operating system its running.
You can even see the Database SQLdbOnLinux that we created by connecting from the PuTTY client.
That’s it for now, will write more about SQL on Linux on coming updates from Microsoft !!!
–> You can also watch this on YouTube: